In the intricate dance of workplace safety, few arenas pose as many challenges as confined spaces. Workers entering these enclosed environments must grapple with various risks, ranging from the insidious threat of toxic gases to the ominous possibility of being locked inside. This comprehensive blog aims to illuminate the multifaceted risks inherent in confined spaces, providing a thorough exploration of the knowledge workers must possess to ensure their safety.
Join us on this enlightening journey as we delve deep into the intricacies of confined space risks, incorporating a focus on key training courses in Surrey.
1. Understanding the Silent Threat: Toxic Gases
Confined spaces, despite their often innocuous appearance, can harbor a silent menace— toxic gases. These invisible, odorless substances pose severe health risks to workers, demanding a nuanced understanding for effective mitigation.
The Confined Space Safety for Monitor and Entrant course, offered by Metro Safety Training, becomes a vital asset in equipping workers to identify, assess, and control the risks associated with toxic gases. By delving into the characteristics and sources of these gases, individuals gain a comprehensive understanding of the invisible threats that can lurk within confined spaces.
The Respiratory Peril: Health Impacts of Toxic Gases
The health impacts of exposure to toxic gases can range from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions. Carbon monoxide, for instance, binds to hemoglobin more readily than oxygen, leading to oxygen deprivation in the body. Hydrogen sulfide, even in low concentrations, can cause respiratory irritation and, in higher concentrations, result in rapid unconsciousness and death.
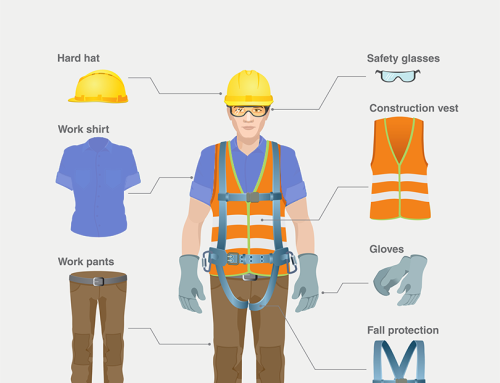
The Confined Space Safety for Monitor and Entrant course not only educates workers about the potential health impacts of exposure but also emphasizes the importance of using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators. Understanding the physiological effects of toxic gases enables workers to make informed decisions and take preventative measures to safeguard their well-being.
2. Navigating Claustrophobia: Physical Hazards in Confined Spaces
The confined nature of spaces introduces a host of physical hazards, creating an environment where risks are ever-present. Entrapment risks and the potential for falling objects are significant concerns that workers must grapple with. In this section, we shed light on the physical challenges faced by workers in confined spaces and highlight the critical role of specialized training.
Metro Safety Training’s Fall Protection course in Surrey emerges as a beacon, providing participants with the skills needed to navigate these hazards safely. From proper equipment usage to effective hazard identification, this training becomes a cornerstone in mitigating physical risks.
Recognizing Claustrophobia in Workers and Implementing Effective Solutions
Recognizing the signs of claustrophobia and implementing effective strategies to address it is crucial for maintaining a safe and productive work environment.
Signs of Claustrophobia
Anxiety and Panic Attacks:
Workers with claustrophobia may experience heightened anxiety or panic attacks when faced with confined spaces. Symptoms include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, sweating, and trembling.
Avoidance Behavior:
Individuals with claustrophobia may actively avoid tasks or assignments that involve working in confined spaces. This avoidance behavior can hinder productivity and compromise the completion of essential job responsibilities.
Irrational Fears:
Workers may express irrational fears related to confined spaces, even when the spaces are not inherently dangerous. These fears can manifest as excessive worry, nervousness, or an overwhelming desire to escape the confined area.
Physical Discomfort:
Claustrophobic individuals may exhibit physical discomfort, such as nausea, dizziness, or a feeling of being trapped when placed in enclosed spaces. These physical reactions can adversely impact their ability to perform tasks effectively.
Difficulty Concentrating:
Workers dealing with claustrophobia may find it challenging to concentrate on their tasks when in confined spaces. This lack of focus can compromise their safety and the safety of those around them.
Dealing with Claustrophobia in Workers:
Open Communication:
Encourage an open dialogue about claustrophobia within the workplace. Foster an environment where workers feel comfortable discussing their concerns and seeking support.
Training and Education:
Provide comprehensive workplace safety training on the nature of claustrophobia, its potential impact on work performance, and strategies for managing the fear. Awareness can be a powerful tool in fostering understanding among coworkers and supervisors.
Gradual Exposure:
Implement a gradual exposure approach for workers dealing with claustrophobia. Gradually introducing them to confined spaces in a controlled and supportive manner can help desensitize the fear over time.
Designated Safe Spaces:
Establish designated safe spaces within confined areas where workers can retreat if they feel overwhelmed. Knowing they have a space to regroup can provide a sense of control and security.
Use of Relaxation Techniques:
Train workers in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or mindfulness, to manage anxiety when confronted with confined spaces. These techniques can be effective in reducing the physiological symptoms of claustrophobia.
Professional Support:
Encourage workers to seek professional support from mental health professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, who specialize in anxiety disorders. Professional guidance can provide tailored strategies for coping with claustrophobia.
Flexible Job Assignments:
Consider flexible job assignments that minimize exposure to confined spaces for workers with severe claustrophobia. This accommodation can help maintain their well-being while ensuring they can contribute effectively to the team.
The Labyrinth of Lock-In: Preventing Entrapment
One of the most unsettling risks within confined spaces is the possibility of being locked inside. This section delves into the intricacies of preventing entrapment, emphasizing the crucial role of comprehensive training. Metro Safety Training’s suite of Occupational First Aid courses, including Levels 1, 2, and 3, as well as the Occupational First Aid Level 3 Pro Renewal, is examined in detail.
These courses empower individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to respond effectively in emergencies, potentially averting dire consequences. Understanding the importance of prompt and effective action is essential in mitigating the risk of entrapment within confined spaces.
Rigorous Hazard Assessments
Conducting rigorous hazard assessments before entering confined spaces is critical. Identify potential entrapment points and develop strategies to mitigate these risks. Regularly reassess the work environment to account for any changes in conditions that may introduce new hazards.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Implement lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that equipment within confined spaces is properly de-energized and isolated before entry. This prevents accidental activation of machinery that could lead to entrapment.
Proper Equipment and PPE
Provide workers with appropriate equipment and personal protective equipment (PPE) designed for confined space entry. This includes harnesses, lifelines, and retrieval systems. Regularly inspect and maintain this equipment to ensure its effectiveness.
Emergency Response Plans
Develop and regularly review emergency response plans specific to confined spaces. Ensure that all workers are familiar with the procedures for evacuating a confined space in the event of an entrapment or other emergencies. Regularly conduct drills to reinforce preparedness.
Permit Systems
Implement a confined space entry permit system. This system should include a thorough review of the work to be performed, identification of potential hazards, and the necessary precautions to prevent entrapment. The permit should be issued only after all safety measures are in place.
Pre-Entry Checklist
Develop a pre-entry checklist that includes a comprehensive review of all safety measures before anyone enters a confined space. This checklist should cover equipment checks, communication systems, and a final confirmation that all necessary precautions are in place.
The Surrey Advantage: Localized Training for Global Safety
Surrey, a dynamic city in Canada, serves as the backdrop for Metro Safety Training’s specialized safety courses. This section emphasizes the localized approach of training, combining theoretical knowledge with practical applications tailored to the unique challenges faced by workers in Surrey.
By immersing participants in real-world scenarios specific to the region, these courses ensure a holistic understanding of confined space risks. The Surrey Advantage not only enhances the effectiveness of training but also strengthens the applicability of learned skills in real work environments.
Bridging Knowledge Gaps: A Deep Dive into Workplace Safety Courses
To further augment our exploration, we look at the Occupational First Aid Level 1, 2, and 3 courses offered by Metro Safety Training. This comprehensive examination aims to empower potential participants with a clear understanding of the benefits these courses bring to their safety repertoire. From basic first aid skills to advanced life-saving techniques, each level contributes to building a resilient and well-prepared workforce. The Occupational First Aid Level 3 Pro Renewal ensures that individuals stay updated and proficient in their life-saving capabilities.
Consider the invaluable courses offered by Metro Safety Training, in partnership with the Canadian Red Cross, as your gateway to enhanced workplace safety. Your safety is our priority—join us in building a secure and resilient workforce.
Contact us today to take the first step towards a safer, more secure workplace.