Falls from heights remain one of the leading causes of serious workplace injuries and fatalities, particularly in construction and industrial settings. While much attention is rightly given to preventing falls in the first place, there’s a lesser-known but equally critical aspect that often gets overlooked: suspension trauma.
Also known as orthostatic intolerance, suspension trauma can lead to potentially life-threatening complications. This blog aims to shed light on the dangers of suspension trauma and how proper fall protection inspection training can save lives.
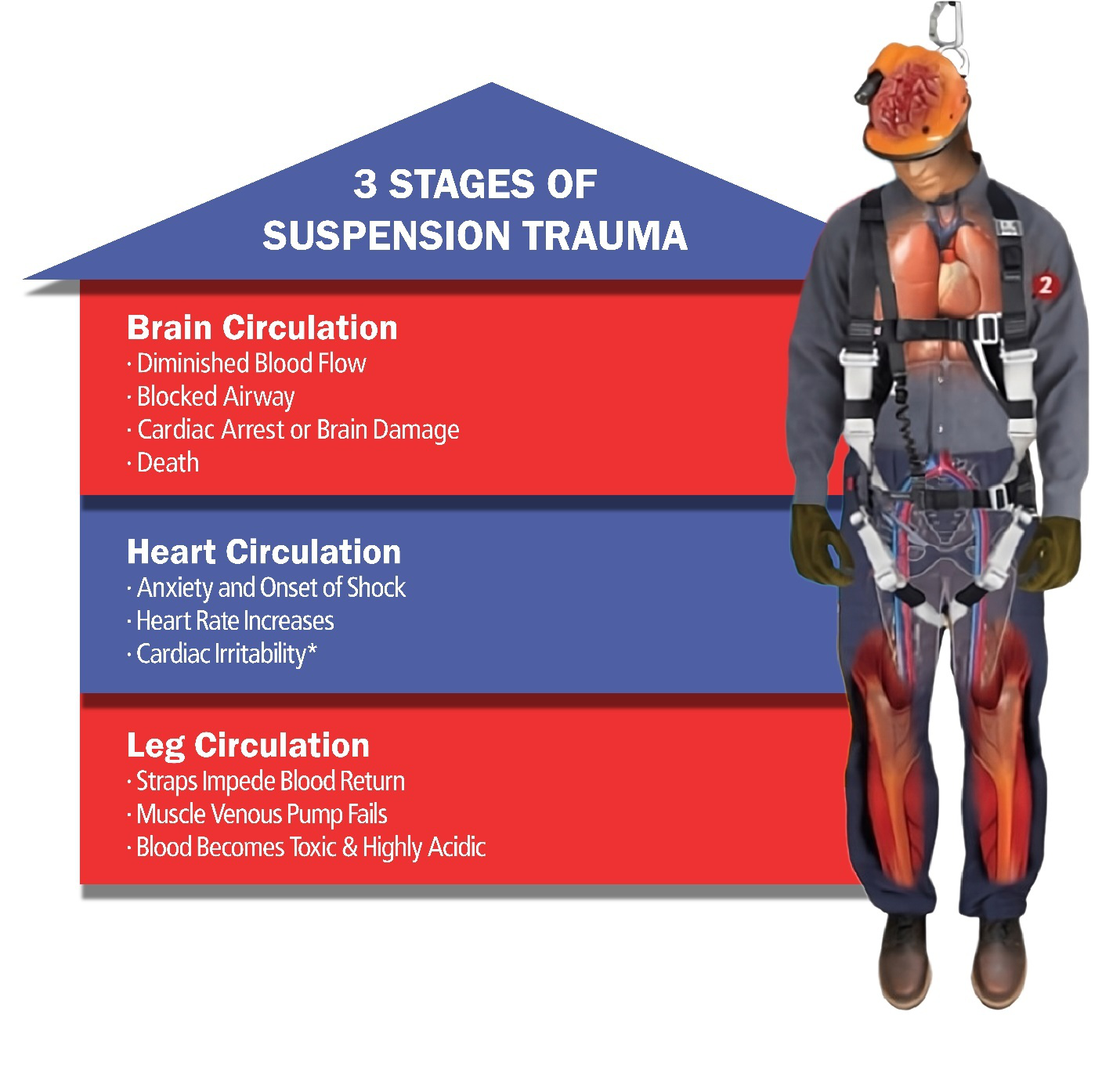
Understanding Suspension Trauma
Suspension trauma happens when a fall protection safety plan successfully stops a fall but leaves the person dangling in a harness. The harness, while preventing a more catastrophic outcome, can restrict blood flow in the legs if the person is immobile for a period.
This lack of movement can lead to the pooling of blood, which reduces the return of blood to the heart and, subsequently, the amount of blood pumped by the heart. If not rescued promptly and properly, this can lead to fainting, organ failure, or even death due to the lack of oxygenated blood reaching critical organs.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Suspension Trauma
When it comes to managing the risks associated with working at heights, understanding and promptly recognizing the signs of suspension trauma is crucial. This condition, while preventable through fall protection training, can escalate quickly if the symptoms are not addressed immediately.
Workers equipped with knowledge from fall protection courses are better prepared to identify and respond to these critical symptoms, which can be the difference between life and death.
Here’s a detailed look at the signs and symptoms of suspension trauma to watch for.
1. Physical Symptoms
The most immediate signs of suspension trauma are physical.
a) Faintness or Lightheadedness
This is often one of the first signs and indicates a decrease in cerebral perfusion, which is the amount of blood flow to the brain.
b) Nausea
As blood pools in the legs and blood flow is compromised, the body may react with feelings of nausea.
c) Breathlessness
An inadequate blood supply can lead to an increased heart rate and shortness of breath as the body attempts to maintain adequate oxygen levels.
d) Paleness of Skin
Reduced blood flow can cause the skin to look notably pale or bluish, especially noticeable in the lips and fingertips.
e) Sweating
Despite a lack of exertion, the individual may begin to sweat profusely; this is a reaction to the body’s stress and the cardiovascular strain.
2. Duration and Severity
The severity and the time frame in which symptoms develop can vary based on several factors, including the individual’s health, the fit and pressure of the harness, and the duration of suspension. It’s important to note that symptoms can worsen rapidly, turning a rescue situation into an emergency medical scenario within minutes.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing suspension trauma begins with comprehensive fall protection coursesand includes several key strategies.
1. Proper Use of Equipment
Ensuring that all fall protection gear is correctly fitted and comfortably worn reduces the risk of severe circulation problems if a fall occurs. Fall protection inspection training teaches workers how to inspect their equipment routinely for any signs of wear or damage that could compromise safety.
2. Training for Quick Rescue
Part of effective fall protection traininginvolves preparing for potential falls, including how to rescue someone quickly and safely. This training is crucial since the quicker a person is rescued after a fall, the lower the risk of suspension trauma.
3. Rescue Plan
Every worksite should have a well-developed rescue plan that is understood and regularly practiced by all team members. This plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a fall, including how to safely lower a suspended worker to the ground.
4. Role of First Aid Training
First aid training courses in Surrey play a critical role in handling suspension trauma cases. Workers trained in level 2 first aid in Surrey are equipped with the skills necessary to provide immediate care after a fall. This includes how to manage shock, ensure clear airways, and facilitate circulation until emergency medical services arrive.
Creating a Comprehensive Fall Protection Safety Plan
A comprehensive fall protection safety plan is a critical component of workplace safety for any organization where employees are exposed to the risks of working at heights. Such a plan not only ensures compliance with safety standards but also establishes a proactive approach to preventing falls and managing the risks associated with them. Here’s how to develop an effective fall protection plan.
1. Hazard Identification
The first step in creating an effective safety plan is the thorough identification of potential fall hazards at the workplace. This includes assessing all areas where work is performed at heights, such as rooftops, ladders, scaffolds, and elevated platforms. Look for risks associated with unstable working surfaces, unprotected edges, or gaps in existing fall prevention measures.
2. Risk Assessment
Once hazards are identified, conduct a detailed risk assessment to evaluate the likelihood of falls and their potential consequences. This process helps prioritize the hazards that need immediate attention and assists in developing specific strategies to mitigate them. Engage employees in this process—they can provide valuable insights into the hazards they face and suggest practical solutions based on their daily experiences.
3. Implementation of Control Measures
Based on the risk assessment, implement appropriate control measures. These can include engineering controls, such as installing guardrails or safety nets, administrative controls, like scheduling work to minimize exposure to risks and providing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as harnesses and lanyards. Training programs such as fall protection trainingand confined spacescourses ensure that workers know how to use the equipment correctly and understand the procedures for working safely.
4. Training and Education
A critical element of the safety plan is comprehensive training for all employees exposed to fall hazards. This should include detailed instructions on the specific hazards they face, the use of necessary protective equipment, and the overall safety practices required on the site. Level 2 first aid training, which covers more advanced first aid practices, is also beneficial in preparing employees to handle any injuries that may occur from falls.
1. Emergency Response and Rescue Plans
Develop and implement emergency response and rescue plans that can be activated in the event of a fall. These plans should outline how to promptly and safely rescue and provide first aid to a fallen worker. Incorporating first aid training courses into your plan ensures that employees are prepared to respond effectively to accidents. Regular drills and practice sessions can help reinforce these plans and ensure that everyone knows their role during an emergency.
2. Monitoring and Review
Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the fall protection measures and the overall safety plan. This should involve regular site inspections, consultations with employees, and reviewing incident reports. Feedback should be used to improve the plan continuously. Also, as part of the ongoing training efforts, consider enrolling employees in first aid training courses to keep their skills sharp and up-to-date.
3. Documentation
Maintain comprehensive documentation of all aspects of the fall protection safety plan, including training records, inspection reports, incident documentation, and revisions to the safety plan. This not only helps in compliance with regulatory requirements but also provides a clear record that can be used for continuous improvement.
Trust Metro Safety
At Metro Safety, we are equipped to provide your staff with the necessary fall protection training to ensure they never experience suspension trauma. This ensures they not only remain safe and healthy but also continue to be active members of your organization. After all, the tragedy of disaster can strike at any time. Would you rather be ready or caught by surprise?
Understanding and preparing for the risks associated with suspension trauma is a critical component of workplace safety for anyone working at heights. By participating in fall protection training, you and your team can enhance your readiness to handle these dangerous situations effectively.
Visit Metro Safety Training today to find out more about our fall protection safety plan and other life-saving courses. Equip yourself with the knowledge and skills to protect not just yourself but also your coworkers from the hidden dangers of falls.