In the realm of industrial workspaces, confined spaces pose unique challenges that demand specialized attention to safety. Workers navigating these confined environments encounter a myriad of risks, ranging from toxic gases to entrapment. In this in-depth exploration, we delve into 15 integral aspects that contribute to enhancing confined space safety.
Anchored in meticulous research and incorporating practical insights, this guide is tailored for professionals seeking a profound understanding of confined space safety protocols.
1. Understanding Confined Spaces
Before delving into safety measures, it’s crucial to comprehend what constitutes a confined space. These are areas with limited entry and exit points, not designed for continuous occupancy. Examples include tanks, silos, and storage bins. Confined spaces may pose atmospheric, physical, or engulfment hazards, necessitating meticulous safety measures.
A comprehensive understanding of confined spaces involves recognizing that these environments vary widely. From the confined spaces in chemical plants to the tight quarters within storage silos, each presents distinct challenges. Workers must identify and assess the specific risks associated with different confined spaces, emphasizing the need for specialized training to navigate these intricacies effectively.
2. Comprehensive Confined Space Safety Training
The foundation of safety in confined spaces lies in comprehensive training. A confined spaces safety training course is essential for workers to grasp the nuances of potential hazards and learn effective mitigation strategies. Metro Safety Training in Vancouver offers specialized courses, including fall protection training in Surrey, OFA training courses, and workplace safety training in Surrey, catering to the diverse needs of industrial professionals.
The cornerstone of confined space safety is education. By incorporating OFA training, Metro Safety ensures that workers are equipped not only to address confined space challenges but also to provide immediate medical assistance when required.
3. Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification
Conducting a thorough risk assessment is paramount before entering a confined space. Identifying potential hazards, whether atmospheric, physical, or biological, enables workers to implement targeted safety measures. This proactive approach is fundamental to preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment.
The art of risk assessment involves a meticulous examination of potential hazards, considering both immediate and latent dangers. Workers trained in this skill can anticipate challenges, whether they stem from atmospheric conditions, physical constraints, or unseen biological factors.
4. Atmospheric Monitoring
Toxic gases and insufficient oxygen levels are common risks in confined spaces. Implementing atmospheric monitoring ensures real-time assessment of air quality. Workers equipped with gas detectors can detect hazardous conditions promptly, allowing for immediate evacuation or the use of appropriate respiratory protection.
Atmospheric monitoring transcends the mere act of checking for gases. It involves a dynamic process of continuous surveillance, utilizing cutting-edge technology to detect even the slightest changes in air quality.
5. Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is essential to maintaining air quality within confined spaces. Employing mechanical ventilation systems, such as blowers or fans, helps mitigate the buildup of hazardous gases and ensures a safe working environment.
Ventilation emerges as a crucial lifeline within confined spaces, transforming potentially hazardous environments into safer workspaces. Beyond the installation of mechanical systems, workers trained in ventilation understand the intricacies of airflow dynamics. They recognize that effective ventilation extends beyond mere air circulation, aiming to disperse contaminants and create a consistently safe atmosphere for prolonged work within confined spaces.
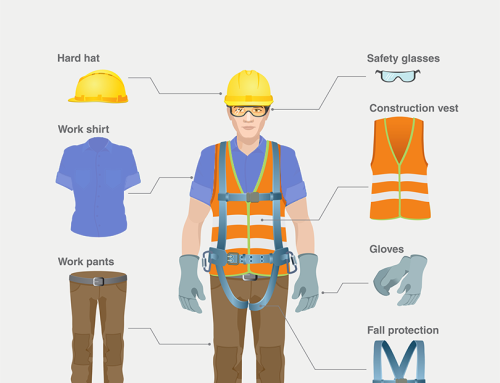
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Selecting and wearing the appropriate PPE is integral to confined space safety. This includes respiratory protection, protective clothing, and other gear designed to safeguard workers against specific hazards. Training programs, such as First Aid Level 1 and Level 2 courses, provide valuable insights into the correct use of PPE.
PPE isn’t just about compliance; it’s a personalized shield against confined space risks. Metro Safety Training’s emphasis on PPE goes beyond routine usage guidelines. Workers are educated on the nuances of selecting PPE tailored to the unique challenges of confined spaces.
7. Confined Space Entry Permits
Establishing a permit system for confined space entry adds an extra layer of safety. Entry permits detail the specific precautions, procedures, and conditions for entry, ensuring that all necessary precautions are in place before workers enter confined spaces.
Entry permits aren’t mere bureaucratic formalities; they are gatekeepers of safety. The meticulous documentation within these permits serves as a roadmap for workers entering confined spaces, guiding them through a series of critical safety checkpoints.
8. Emergency Response Planning
Preparing for emergencies is a fundamental aspect of confined space safety. Establishing clear emergency response plans, conducting regular drills, and ensuring that workers are well-versed in evacuation procedures are critical components of a robust safety strategy.
Emergency response planning transcends theoretical scenarios; it’s a dynamic blueprint for real-time action. Metro Safety Training’s approach to emergency preparedness is rooted in practicality. Workers aren’t just familiarized with protocols; they actively participate in realistic drills that simulate confined space emergencies. This hands-on experience not only enhances response efficiency but also cultivates a collective mindset where every worker becomes a vigilant participant in ensuring the safety of their team.
9. Proper Training for Emergency Situations
In the event of an emergency, proper training can be the difference between a controlled response and chaos. First Aid Level 1 and Level 2 courses equip workers with the knowledge and skills to provide immediate medical assistance in confined spaces until professional help arrives.
First Aid training at Metro Safety goes beyond the basics; it’s a lifeline in confined spaces. Workers aren’t just taught to respond; they are instilled with the confidence to act decisively in high-pressure situations.
10. Communication Protocols
Clear communication is essential in confined spaces where visibility and access may be limited. Implementing effective communication protocols, such as two-way radios or signaling systems, ensures that workers can convey information and receive instructions without delay.
Communication within confined spaces isn’t just about exchanging information; it’s a lifeline that connects the workforce. Metro Safety Training recognizes that effective communication protocols extend beyond devices; they include the development of a shared language that transcends verbal cues. Workers are trained not just in the operation of communication tools but in the art of concise and unambiguous communication, fostering an environment where every word matters in ensuring the safety of all team members.
11. Continuous Monitoring During Entry
Once inside a confined space, continuous monitoring is imperative. This includes keeping an eye on atmospheric conditions, the well-being of workers, and any changes in the confined space environment. Real-time monitoring allows for swift response to evolving situations.
Continuous monitoring isn’t a passive task; it’s an ongoing commitment to worker safety. Metro Safety Training emphasizes that monitoring extends beyond periodic checks; it involves a dynamic, real-time engagement with the confined space environment.
12. Prevention of Engulfment Hazards
Engulfment hazards, where a worker may be surrounded by or submerged in a liquid or flowing substance, require specialized attention. Implementing preventive measures, such as barriers and lockout/tagout procedures, is crucial to mitigating engulfment risks.
Engulfment hazards demand more than awareness; they necessitate a proactive stance against potential catastrophes. Workers are trained not only in the technicalities of barriers and lockout/tagout but in cultivating a mindset that places prevention at the forefront. This foresight transforms confined spaces into safer environments where engulfment hazards are systematically neutralized.
13. Confined Space Rescue Procedures
Developing and practicing confined space rescue procedures is a non-negotiable aspect of safety. Workers should be trained in rescue techniques, and the availability of rescue equipment, such as tripods and hoists, should be ensured.
Confined space rescue isn’t a contingency plan; it’s an integral part of the safety fabric.
14. Regular Safety Inspections
Routine inspections of confined spaces and associated safety equipment are vital for identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate. This includes checking the integrity of barriers, ventilation systems, and emergency response equipment.
Safety inspections aren’t just about compliance; they are proactive guardians of worker well-being. Metro Safety Training instills a culture of regular inspections that go beyond ticking boxes. Workers are educated to view inspections as opportunities to fine-tune safety measures, ensuring that every component within a confined space is not just functional but optimized for the dynamic challenges of industrial work. By fostering a mindset of continuous improvement, Metro Safety Training ensures that confined spaces remain not just safe but evolve to meet the ever-changing demands of worker safety.
15. Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintaining comprehensive documentation is not only a regulatory requirement but a valuable tool for continuous improvement. Keeping records of training, risk assessments, permits, and emergency response drills allows for the review and refinement of safety protocols.
Contact Metro Safety Training today to elevate your confined space safety protocols and ensure a secure working environment. Your safety is our priority.
Note: This blog serves as an informative guide and should not replace specific training or advice from safety professionals. Always adhere to local regulations and seek guidance from qualified safety experts.