Confined spaces present a unique set of hazards that can pose serious risks to workers. Effective confined space training is crucial for mitigating these risks and ensuring safe entry and rescue operations.
This blog will discuss the unique hazards of confined spaces, regulatory requirements in Canada, and effective training strategies to ensure worker safety. It will also explore the benefits of worker safety training programs like confined space training, fall protection training, first aid training in Vancouver, and more.
Unique Hazards Associated with Confined Spaces
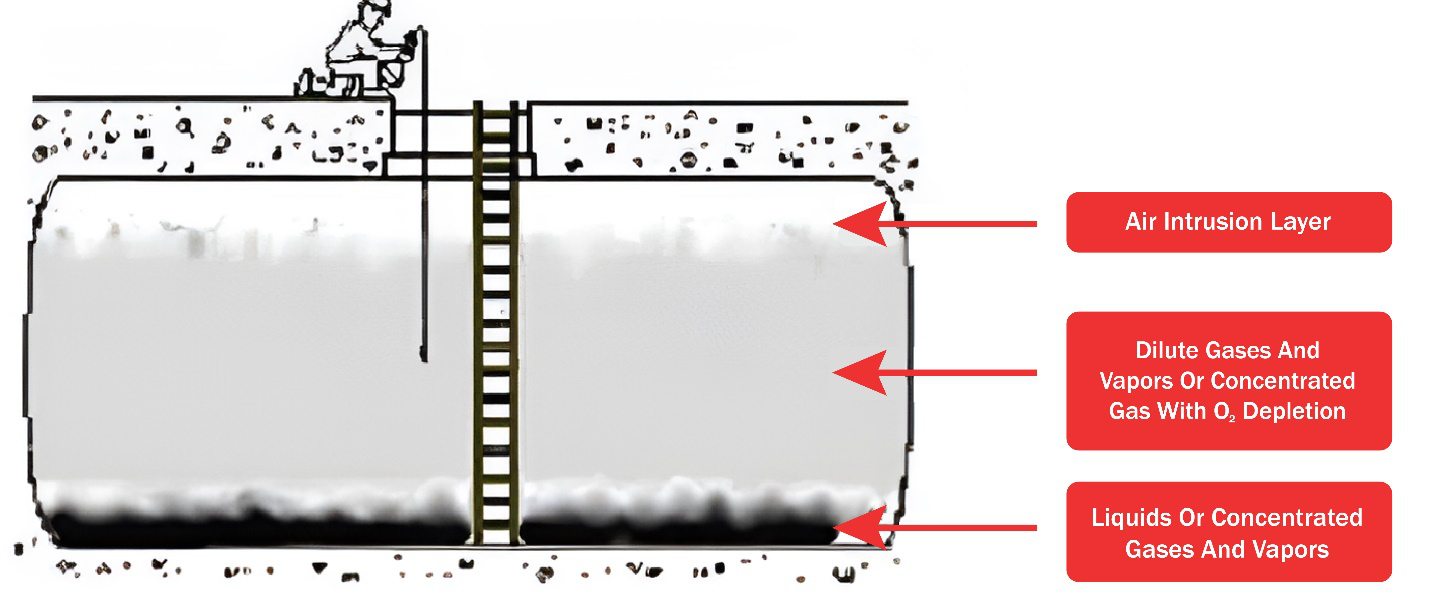
Confined spaces are defined as areas that are not designed for continuous occupancy, have limited or restricted means of entry or exit, and are large enough for a worker to enter and perform tasks. These spaces can include tanks, silos, storage bins, vaults, and pits. The unique hazards of confined spaces make them particularly dangerous:
Common Hazards in Confined Spaces
- Oxygen Deficiency: Confined spaces can have low levels of oxygendue to poor ventilation, leading to suffocation.
- Toxic Atmospheres: Hazardous gases and vapors can accumulate in confined spaces, posing a risk of poisoning.
- Flammable Atmospheres: The presence of flammable gases, vapors, or dust can create a risk of explosions or fires.
- Engulfment: Workers can be engulfed by loose materials such as grain, sand, or liquids, leading to suffocation or crushing injuries.

- Mechanical Hazards: Moving parts of machinery or equipment within confined spaces can cause injuries.
- Physical Hazards: Confined spaces may have poor lighting, slippery surfaces, or sharp edges, increasing the risk of slips, trips, and falls.
Regulatory Requirements for Confined Space Safety in Canada
In Canada, confined space safety is regulated by provincial and territorial occupational health and safety (OHS) legislation. Employers are required to identify confined spaces, assess the risks, and implement control measures to protect workers. Key regulatory requirements include:
1. Hazard Assessment
Employers must conduct a thorough hazard assessment for each confined space to identify potential risks and determine appropriate control measures. The assessment should consider factors such as:
- Atmospheric hazards (e.g., oxygen deficiency, toxic gases)
- Physical hazards (e.g., poor lighting, slippery surfaces)
- Engulfment hazards(e.g., loose materials)
- Mechanical hazards (e.g., moving parts of equipment)
2. Written Confined Space Program
Employers must develop a written confined space program that outlines procedures for safe entry, work, and rescue operations. The program should include:
- Hazard identification and assessment
- Entry permit system
- Atmospheric testing and monitoring
- Ventilation and purging
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Emergency response and rescue procedures
3. Entry Permit System
A confined space entry permit system is required to ensure that all necessary precautions are taken before workers enter a confined space. The permit should include:
- Identification of the confined space
- List of authorized entrants and attendants
- Description of the work to be performed
- Hazard assessment and control measures
- Atmospheric testingresults
- Required PPE
- Emergency response and rescue procedures
4. Atmospheric Testing and Monitoring
Atmospheric testing and monitoring are critical to ensure that the air quality in a confined space is safe for workers. Employers must:
- Test for oxygen levels, toxic gases, and flammable atmospheres before entry
- Continuously monitor the atmosphere during work
- Use appropriate testing equipment and procedures
5. Ventilation and Purging
Proper ventilation and purging are necessary to maintain safe air quality in confined spaces. Employers should:
- Use mechanical ventilation to provide fresh air and remove hazardous gases
- Purge confined spaces with inert gas or air to eliminate flammable or toxic atmospheres

6. Training and Competency
Employers must ensure that workers and supervisors are trained and competent in confined space safety. Training should cover:
- Hazard recognition and assessment
- Safe work procedures
- Use of PPE and safety equipment
- Atmospheric testing and monitoring
- Emergency response and rescue procedures
Effective Training Strategies for Confined Space Safety
Effective confined space safety training is essential to equip workers with the knowledge and skills to recognize hazards, use safety equipment, and respond to emergencies. Key training strategies include:
Comprehensive Training Programs
A comprehensive confined space training program should cover all aspects of confined space safety, including:
- Hazard identification and assessment
- Entry permit system
- Atmospheric testing and monitoring
- Ventilation and purging
- Use of PPE and safety equipment
- Emergency response and rescue procedures
Refresher Training
Regular refresher training is necessary to keep workers’ knowledge and skills up-to-date. Refresher training should be conducted:
- Annually or as required by regulations
- When there are changes to work procedures, equipment, or hazards
- After an incident or near-miss
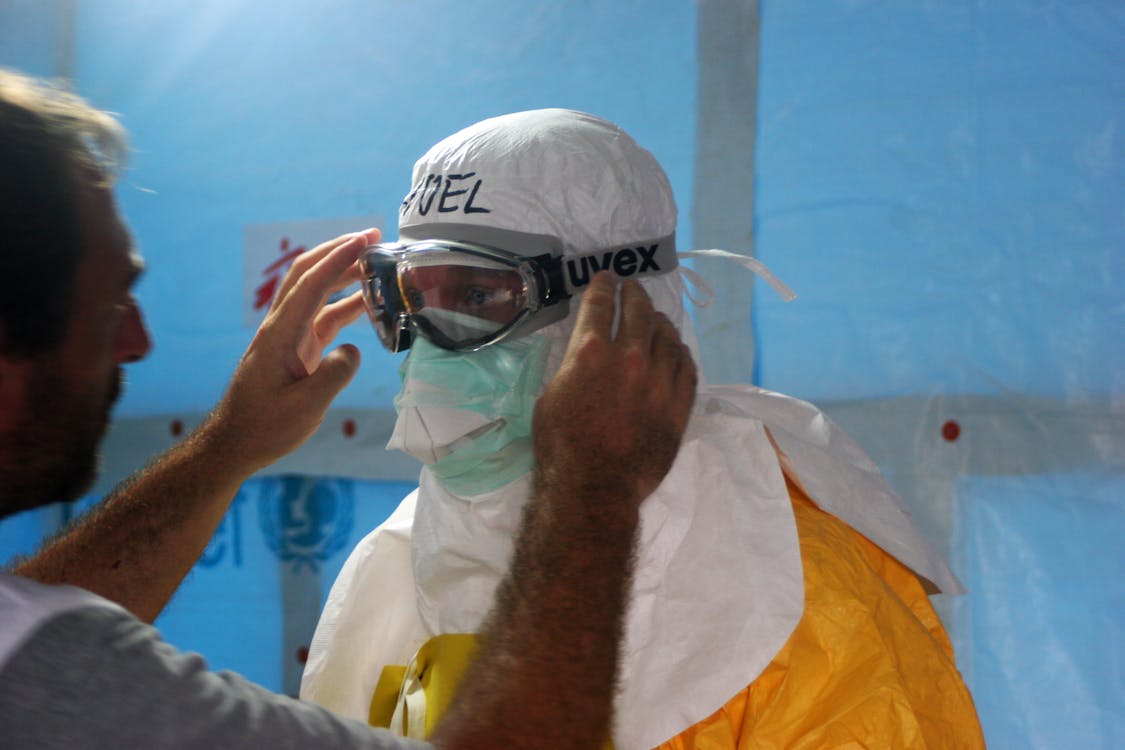
Role of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in Confined Space Safety
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in protecting workers from hazards in confined spaces. Key types of PPE for confined space entry include:
Respiratory Protection
Respiratory protection is essential for protecting workers from inhaling hazardous gases, vapors, and particulates. Types of respiratory protection include:
- Air-Purifying Respirators(APRs): Remove contaminants from the air using filters or cartridges.
- Supplied-Air Respirators(SARs): Provide clean air from a remote source through a hose.
- Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus(SCBA): Provide clean air from a portable tank.
Head, Eye, and Face Protection
Head, eye, and face protection are necessary to protect workers from physical hazards and chemical exposures. Types of protection include:
- Hard Hats: Protect the head from impact and falling objects.
- Safety Glasses and Goggles: Protect the eyes from dust, debris, and chemical splashes.
- Face Shields: Protect the face from chemical splashes and flying debris.
Hand and Body Protection
Hand and body protection are essential for protecting workers from cuts, abrasions, chemical exposures, and thermal hazards. Types of protection include:
- Gloves: Protect the hands from cuts, abrasions, and chemical exposures. Types of gloves include chemical-resistant gloves, cut-resistant gloves, and heat-resistant gloves.
- Coveralls and Suits: Protect the body from chemical splashes, thermal hazards, and physical hazards. Types of coveralls and suits include disposable coveralls, chemical-resistant suits, and flame-resistant suits.
Emergency Response and Rescue Procedures
Effective emergency response and rescue procedures are crucial for ensuring the safety of workers in confined spaces. Key components of emergency response and rescue procedures include:
Emergency Planning
Emergency planning involves developing a comprehensive plan for responding to confined space emergencies. The plan should include:
- Procedures for raising the alarm and summoning emergency services
- Roles and responsibilities of emergency response personnel
- Communication protocols
- Evacuation routes and procedures
Rescue Equipment
Rescue equipment is essential for safely rescuing workers from confined spaces. Key types of rescue equipment include:
- Rescue Harnesses and Lanyards: Used to lift and lower workers during rescue operations.
- Tripods and Davit Systems: Provide stable anchor points for rescue operations.
- Rescue Stretchers and Baskets: Used to transport injured workers to safety.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
First aid training courses are essential for equipping workers with the knowledge and skills needed to provide immediate medical assistance in the event of an injury or illness. Metro Safety Training offers a range of first aid training courses in Surrey, including:
Occupational First Aid Level 1
Occupational First Aid Level 1 provides basic first aid training for workers in low-risk environments. The course covers:
- Assessing and managing medical emergencies
- Administering CPR and using an automated external defibrillator (AED)
- Treating minor injuries such as cuts, bruises, and burns
Occupational First Aid Level 2
Occupational First Aid Level 2 provides advanced first aid training for workers in medium-risk environments. The course covers:
- Conducting a primary and secondary assessment
- Managing medical emergencies and providing life-saving interventions
- Treating injuries such as fractures, sprains, and head injuries
Occupational First Aid Level 3
Occupational First Aid Level 3 provides comprehensive first aid training for workers in high-risk environments. The course covers:
- Conducting a thorough patient assessment and providing advanced medical care
- Managing complex medical emergencies and multiple casualties
- Administering medications and using advanced medical equipment
Occupational First Aid Level 3 Pro Renewal
Occupational First Aid Level 3 Pro Renewal is designed for workers who need to renew their Level 3 certification. The course covers:
- Reviewing and updating first aid knowledge and skills
- Practicing advanced medical interventions and procedures
- Demonstrating competency in providing first aid care
Confined Space Training in Vancouver
Metro Safety Training offers confined space training in Vancouver to equip workers with the knowledge and skills needed to safely enter and work in confined spaces. The training covers:
Hazard Identification and Assessment
Workers learn to identify and assess hazards associated with confined spaces, including:
- Atmospheric hazards (e.g., oxygen deficiency, toxic gases)
- Physical hazards (e.g., poor lighting, slippery surfaces)
- Engulfment hazards (e.g., loose materials)
- Mechanical hazards (e.g., moving parts of equipment)
Emergency Response and Rescue
Workers learn emergency response and rescue procedures for confined space incidents, including:
- Raising the alarm and summoning emergency services
- Using rescue equipment and techniques
- Providing first aid and medical assistance to injured workers
Ensure your workers are well-prepared and compliant with the latest safety standards by enrolling them in our comprehensive training programs. Visit our website to learn more about our confined spacetraining in Vancouver, fall protection courses, and first aid training courses in Surrey.
Enhance your workplace safety today with Metro Safety Training. Contact us now to enroll in our confined space safety training and other safety courses. Together, we can create a safer work environment for everyone.