Workplace safety is a critical concern in every industry, with employers striving to create environments that protect their workers from both immediate hazards and long-term health issues. While much attention is given to training employees in safety procedures, such as first aid training courses, and equipping them with protective gear, the importance of ergonomic safety, particularly through comfortable work seating, needs to be addressed. Poor seating can lead to a variety of musculoskeletal problems, resulting in discomfort, decreased productivity, and long-term health issues for employees.
This blog will explore the ergonomic risks associated with inadequate seating and provide a comprehensive guide on how to create a safe and comfortable work environment through proper seating arrangements. By addressing these risks, businesses can ensure that their employees are not only safe but also comfortable and productive.
Understanding Ergonomic Risks in the Workplace:
Ergonomic risks refer to potential hazards in the workplace that can harm workers through repetitive strain, poor posture, and other physical stressors. One of the most common sources of these risks is inadequate or improperly designed seating. Chairs that lack proper support are incorrectly adjusted or do not accommodate the worker’s body can lead to a range of health issues, from back pain to carpal tunnel syndrome.
The problem is exacerbated in environments where employees are required to sit for long periods, such as in offices or control rooms. Without comfortable work seating, the prolonged strain on the body can lead to chronic pain and injuries, which can decrease employee morale, increase absenteeism, and even result in workers’ compensation claims.
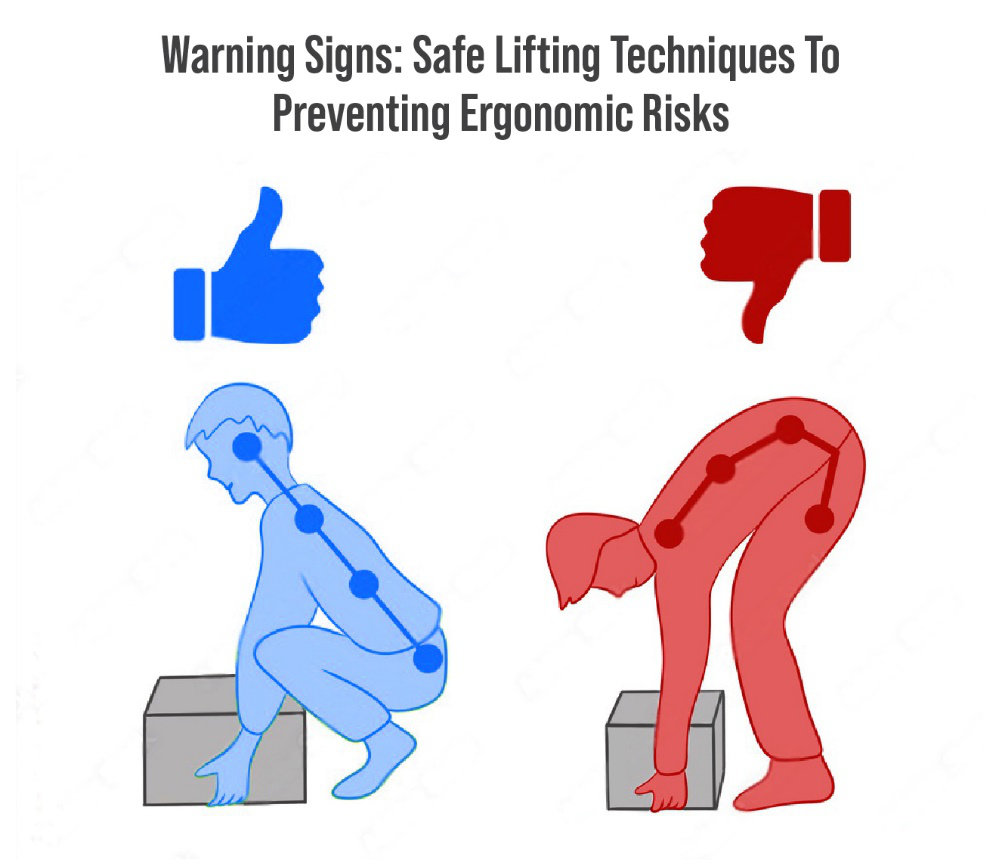
The Impact of Poor Seating on Workers’ Health:
When employees are forced to sit in poorly designed chairs, their bodies compensate by adopting unnatural postures. Over time, this can lead to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), which are injuries or disorders affecting the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage, and spinal discs. MSDs are often caused by repetitive strain, overexertion, or prolonged static postures—all of which can result from poor seating arrangements.
For instance, an office worker sitting in a chair without adequate lumbar support may develop lower back pain due to the constant strain placed on the spine. Similarly, a factory worker using a chair that is too high or too low may experience neck and shoulder pain from continually having to adjust their posture to see their work. These issues are not just painful but can lead to long-term health problems, reducing the overall quality of life for the worker.
Key Elements of Comfortable Work Seating:
To address these ergonomic risks, it is essential to focus on providing comfortable work seating that supports the worker’s body and reduces the likelihood of injury. The following are key elements to consider when selecting and setting up seating for employees:
Adjustability: Chairs should be highly adjustable to accommodate the diverse body types of workers. This includes the ability to adjust the height, backrest angle, armrests, and seat depth. Proper adjustability allows workers to modify their seating to fit their individual needs, promoting better posture and reducing strain.
Lumbar Support: A good chair should provide adequate support for the lower back. Lumbar support helps maintain the natural curve of the spine, preventing slouching and reducing the risk of lower back pain. The lumbar support must be adjustable to ensure it fits the curvature of the worker’s spine correctly.
Seat Depth and Width: The seat should be deep and wide enough to comfortably accommodate the worker. A seat that is too shallow can cause pressure on the thighs, while one that is too deep can force the worker to sit forward, leading to slouching and back pain. Ideally, there should be a small gap between the edge of the seat and the back of the knees.
Armrests: Armrests should support the arms without causing the shoulders to rise. They should be adjustable in height and width to allow the worker’s arms to rest comfortably at their sides with the elbows at a 90-degree angle.
Material and Padding: The chair’s material should be breathable to prevent discomfort from heat and perspiration. Adequate padding is also necessary to provide comfort, but it should not be so soft that it offers little support or so firm that it causes pressure points.
Creating a Safe and Comfortable Work Environment:
Providing comfortable work seating is just one aspect of creating an ergonomic workspace. Employers should also consider the overall layout of the workspace to ensure that it complements the seating arrangements and promotes good posture.
Workstations should be designed to allow workers to maintain a neutral posture, where the spine is aligned and the joints are not under strain. The height of desks and work surfaces should be adjustable or appropriately matched to the seating to prevent workers from hunching over or reaching too high. Moreover, work tasks should be organized to minimize repetitive movements and encourage movement breaks to reduce the risk of strain injuries.
First aid training courses, including advanced first aid courses and intermediate first aid courses, can also play a critical role in addressing ergonomic risks. By educating employees on how to recognize the early signs of strain and injury, they can take proactive steps to adjust their work environment or seek medical advice before a minor issue becomes a major problem.
The Role of Training in Preventing Ergonomic Injuries:
In addition to providing proper seating, employers should invest in training programs to educate their workforce about the importance of ergonomics. Courses like fall protection training and confined space training are vital for preventing physical injuries in hazardous environments, but ergonomic training is equally important for preventing injuries in more sedentary work settings.
Training should focus on teaching workers how to adjust their seating and workstations to fit their bodies, recognize the signs of ergonomic strain, and practice good posture throughout the day. This knowledge empowers employees to take control of their own health and well-being, reducing the risk of long-term injuries.
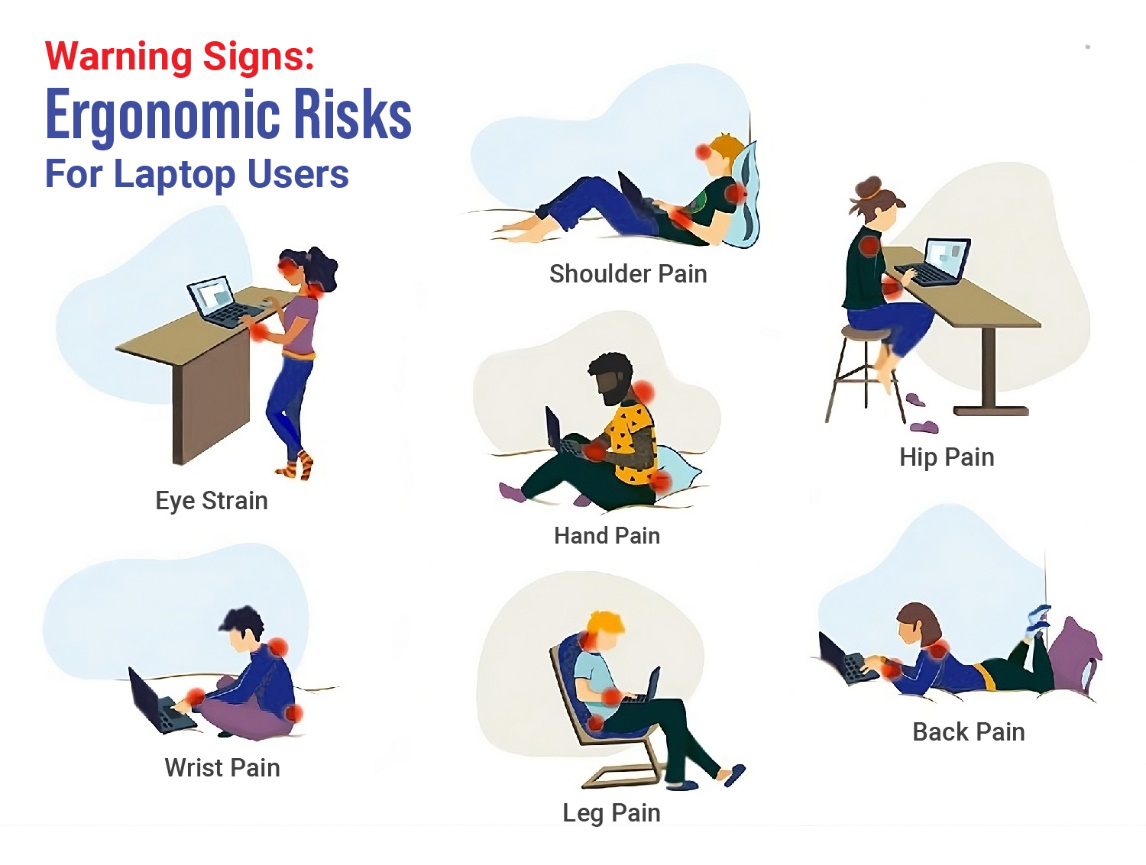
The Benefits of Addressing Ergonomic Risks:
Investing in comfortable work seating and ergonomic training benefits employees and provides significant advantages for employers. By reducing the risk of MSDs and other ergonomic-related injuries, businesses can decrease absenteeism and workers’ compensation claims. Additionally, employees who are comfortable and pain-free are more likely to be productive, engaged, and satisfied with their jobs.
A well-thought-out ergonomic plan also demonstrates a company’s commitment to its employees’ health and safety. This can improve the organization’s reputation, making it more attractive to potential hires and increasing employee retention rates.
Implementing Ergonomic Solutions in the Workplace:
Implementing ergonomic solutions, including comfortable work seating, requires a comprehensive approach. Employers should start by assessing the current work environment to identify potential ergonomic risks. This can be done through workplace evaluations, employee surveys, and consultation with ergonomic experts.
Once risks have been identified, employers should take immediate steps to address them. This might involve purchasing new ergonomic chairs, reconfiguring workstations, or providing additional training on proper posture and workstation setup.
Regular follow-ups and adjustments are also necessary as the workforce changes and new risks emerge. By continually assessing and improving the work environment, employers can ensure that their ergonomic solutions remain effective in preventing injuries and promoting comfort.

Creating a Safer and More Comfortable Workplace:
Ergonomics is an often overlooked aspect of workplace safety, but it plays a crucial role in protecting employees from long-term health issues. By focusing on comfortable work seating and providing the necessary training and resources, employers can create a work environment that not only keeps their employees safe but also enhances their comfort and productivity.
Whether it’s through first aid training courses, basic first aid training, intermediate first aid courses, or specialized programs like fall protection training and confined space training, Metro Safety Training in Vancouver and Surrey is dedicated to helping businesses create safer work environments.
Don’t wait for a catastrophe. For comprehensive training and ergonomic assessments, contact Metro Safety Training today to ensure your employees are protected and comfortable.







