Working in extreme temperatures poses significant risks to employee health and safety. Heat stress, which occurs when the body cannot cool itself adequately, can lead to severe health issues, decreased productivity, and even fatalities.
This comprehensive blog explores the risks of heat stress in workplaces, training programs for heat stress prevention, and measures to ensure worker safety in hot environments.
What is Heat Stress?
Heat stress occurs when the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature due to external heat sources, strenuous physical activity, or a combination of both. It can lead to heat-related illnesses such as heat rash, heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke.
Causes of Heat Stress
Several factors contribute to heat stress, including:
- High Ambient Temperatures:Hot weather conditions significantly increase the risk.
- Humidity:High humidity levels hinder the body’s ability to sweat and cool down.
- Physical Exertion:Strenuous activities increase the body’s heat production.
- Inadequate Hydration:Dehydration impairs the body’s cooling mechanisms.
- Inappropriate Clothing:Wearing heavy or non-breathable clothing traps heat.
Symptoms of Heat Stress

Recognizing the symptoms of heat stress is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive sweating
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion or disorientation
- Fainting
Risks of Heat Stress in Workplaces
Health Risks
Heat stress poses significant health risks to workers, particularly those in industries such as construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and outdoor services. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can lead to:
- Heat Rash:Skin irritation caused by excessive sweating.
- Heat Cramps:Painful muscle contractions due to electrolyte imbalances.
- Heat Exhaustion:A condition characterized by heavy sweating, weakness, and nausea.
- Heat Stroke:A life-threatening condition where the body’s temperature regulation fails, leading to high body temperatures, confusion, and unconsciousness.
Productivity and Safety Risks
Heat stress not only affects health but also impacts workplace productivity and safety:
- Decreased Productivity:Workers experiencing heat stress are less efficient and may require more frequent breaks.
- Increased Accidents:Heat stress can impair cognitive and motor functions, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Higher Absenteeism:Heat-related illnesses can lead to increased absenteeism, affecting overall workforce availability.
Heat Stress Training Programs
Importance of Heat Stress Training
Implementing effective heat stress training programs is essential for preventing heat-related illnesses and ensuring worker safety. Training programs should educate workers and supervisors on recognizing, preventing, and managing heat stress.

Components of Heat Stress Training
Understanding Heat Stress
- Educate workers on the causes, symptoms, and health risks of heat stress.
Risk Assessment
- Conduct assessments to identify high-risk areas and tasks.
- Evaluate environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and heat sources.
Preventive Measures
- Implement engineering controls, such as ventilation and shading, to reduce heat exposure.
- Encourage workers to wear appropriate clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Hydration and Rest
- Promote regular hydration breaks and provide access to cool drinking water.
- Schedule rest breaks in shaded or air-conditioned areas.
First Aid Training
- Train workers in Standard first aidand Emergency First Aid and CPR to handle heat-related emergencies.
- Ensure availability of Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3certified personnel.
Emergency Procedures
- Develop and communicate emergency response plans for heat-related incidents.
- Conduct drills to ensure workers are prepared to respond effectively.
Specialized Training Programs
Fall Protection Training
- Heat stress can increase the risk of falls. Fall protection trainingensures workers are equipped with the knowledge and skills to prevent falls, especially in hot environments.
Confined Space Training in Vancouver
- Working in confined spaces can exacerbate heat stress. Confined space training in Vancouverprepares workers to safely navigate and work in confined spaces while managing heat risks.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
- Comprehensive first aid training courses in Surreyprovide workers with the skills to administer immediate care in case of heat-related emergencies.
Measures to Ensure Worker Safety in Hot Environments
Engineering Controls
Ventilation:
- Improve air circulation using fans or exhaust systems to reduce heat buildup.
- Use portable air conditioning units in enclosed or high-risk areas.
Shading:
- Provide shaded areas or canopies to protect workers from direct sunlight.
- Use reflective or light-colored materials to reduce heat absorption.
Insulation:
- Insulate hot surfaces and equipment to minimize heat exposure.
- Use thermal barriers or reflective coatings on roofs and walls.
Administrative Controls
Work Schedules:
- Schedule physically demanding tasks during cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon.
- Rotate workers to minimize prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Rest Breaks:
- Implement mandatory rest breaks in cool or shaded areas to prevent overheating.
- Encourage workers to take additional breaks if they feel fatigued or overheated.
Hydration Policies:
- Establish hydration stations with cool drinking water throughout the worksite.
- Encourage workers to drink water frequently, even if they are not thirsty.

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Lightweight Clothing:
- Encourage workers to wear lightweight, breathable clothing to enhance heat dissipation.
- Provide moisture-wicking and UV-protective clothing
Cooling Vests:
- Use cooling vests or bandanas to help regulate body temperature in extreme heat.
- Provide access to personal cooling devices, such as neck fans or cooling towels.
Sun Protection:
- Provide and encourage the use of wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and sunscreen to protect against sun exposure.
The Role of First Aid in Heat Stress Management
Standard First Aid and Emergency First Aid and CPR
Standard first aid and Emergency First Aid and CPR training are critical for managing heat stress in the workplace. These training programs equip workers with the knowledge and skills to provide immediate care in case of heat-related emergencies.
Recognizing Symptoms:
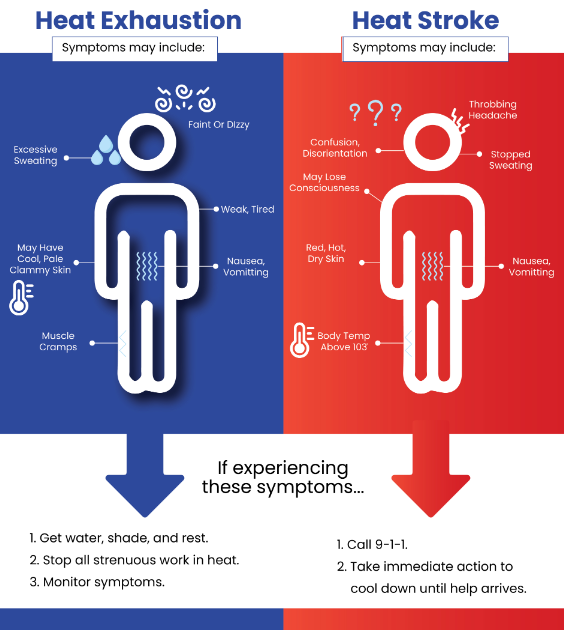
- Train workers to recognize the symptoms of heat stress and differentiate between heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
Providing Immediate Care:
- Teach workers how to administer first aid for heat stress, including cooling techniques and hydration methods.
- Ensure workers know how to perform CPR and use AEDs in case of heat-related cardiac emergencies.
Emergency Procedures:
- Develop clear emergency response procedures for heat-related incidents.
- Conduct regular drills to ensure workers are prepared to respond quickly and effectively.
Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3
Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3 training provides a comprehensive approach to workplace first aid, covering a wide range of medical emergencies, including heat stress.
Basic First Aid (Level 1):
- Provides fundamental skills for managing minor injuries and heat-related illnesses.
- Ensures workers can provide initial care and stabilize patients until professional help arrives.
Intermediate First Aid (Level 2):
- Covers more advanced first aid techniques and procedures.
- Includes training on handling more severe heat stress cases and other medical emergencies.
Advanced First Aid (Level 3):
- Provides in-depth training on complex medical emergencies and advanced first aid procedures.
- Prepares workers to manage critical heat stress incidents and coordinate with emergency medical services.
Integrating Heat Stress Management with Comprehensive Safety Training
Fall Protection Training
Fall protection training is essential for preventing falls, especially in hot environments where heat stress can impair balance and coordination. This training ensures workers understand the risks of falls and are equipped with the necessary skills and equipment to work safely at heights.
- Risk Assessment:
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify fall hazards in hot environments.
- Implement measures to mitigate risks, such as installing guardrails and safety nets.
- Use of PPE:
- Train workers to use fall protection equipment, such as harnesses and lanyards, correctly.
- Ensure equipment is regularly inspected and maintained.
- Emergency Procedures:
- Develop and communicate clear procedures for responding to fall incidents.
- Conduct regular drills to ensure workers are prepared to handle fall emergencies.
Confined Space Training in Vancouver
Confined space training in Vancouver is crucial for workers who operate in confined spaces, where heat stress can be exacerbated by poor ventilation and limited air circulation. This training prepares workers to safely navigate and work in confined spaces while managing heat risks.
- Risk Assessment:
- Conduct risk assessments to identify confined spaces and evaluate heat stress risks.
- Implement measures to improve ventilation and reduce heat buildup.
- Entry Procedures:
- Train workers on proper entry and exit procedures for confined spaces.
- Ensure workers understand the importance of continuous monitoring and communication.
- Emergency Procedures:
- Develop and communicate emergency response plans for confined space incidents.
- Conduct regular drills to ensure workers are prepared to respond effectively.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
First aid training courses in Surrey provide comprehensive training on handling a wide range of medical emergencies, including heat stress. These courses ensure workers are equipped with the skills to provide immediate care and stabilize patients until professional help arrives.
- Basic First Aid:
- Covers fundamental skills for managing minor injuries and heat-related illnesses.
- Ensures workers can recognize symptoms and administer initial care.
- Advanced First Aid:
- Provides more in-depth training on handling severe heat stress cases and other medical emergencies.
- Prepares workers to coordinate with emergency medical services and provide advanced care.
Ensure your workplace is prepared for extreme temperatures with comprehensive safety training programs from Metro Safety Training. Our expert-led courses, including heat stress training, fall protection training, confined space training in Vancouver, first aid training courses in Surrey, and Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3, provide the knowledge and skills necessary to keep your workers safe. Contact us today to learn more about our Occupational First Aid courses in BC, Standard first aid, and Emergency First Aid and CPR programs. Invest in your workers’ safety and well-being with Metro Safety Training.







