Electrical hazards are one of the leading causes of workplace injuries and fatalities. The complexity and danger of electrical systems necessitate a robust understanding of safe work practices and compliance with safety regulations.
This blog will outline the risks associated with electrical hazards, the importance of comprehensive workplace safety training, and the necessary steps to ensure a safe working environment.
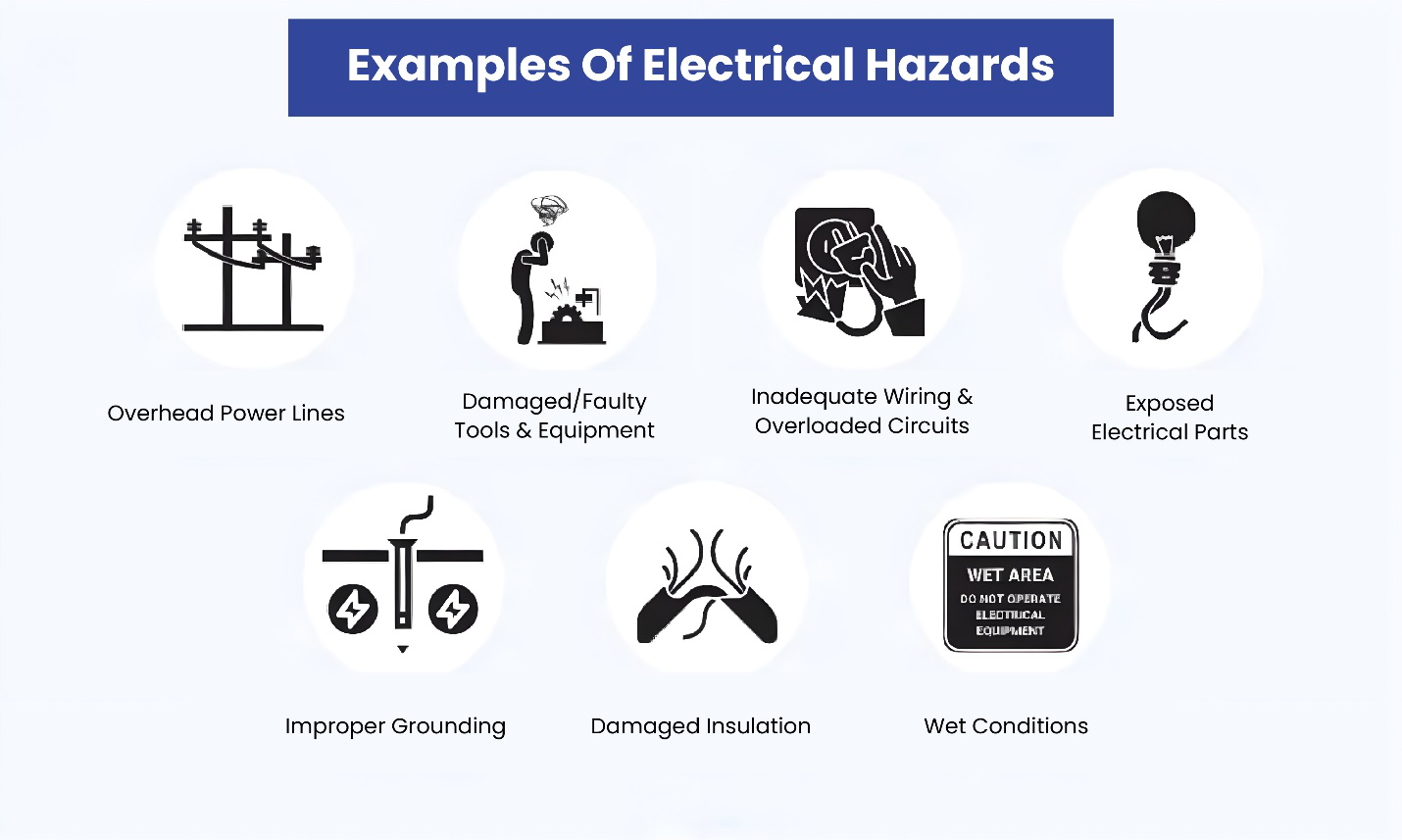
Understanding Electrical Hazards
Common Electrical Hazards
- Electrical Shock: Contact with live electrical parts can cause serious injuries or even death. Electrical shock can occur when an individual touches an energized part or circuit.
- Arc Flash: An arc flash is a sudden release of electrical energy through the air, caused by a fault. It can result in severe burns, fire, and even explosions.
- Arc Blast: This is the explosive expansion of air due to the intense heat generated by an arc flash. The blast can propel objects and cause significant injuries.
- Electrical Burns: These burns result from contact with energized electrical partsor from arc flash incidents.
- Fire and Explosions: Faulty electrical installations, overloaded circuits, and damaged wiring can lead to fires and explosions.
Consequences of Electrical Incidents
Electrical incidents can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Injuries and Fatalities: Electrical hazards can cause serious injuries, permanent disabilities, and fatalities.
- Property Damage: Fires and explosions caused by electrical faults can result in extensive property damage.
- Operational Downtime: Electrical incidents can disrupt operations, leading to significant downtime and financial losses.
- Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with electrical safety regulations can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
Train your workers for occupation first aid and emergency response to minimize injury and fatality risks.
Importance of Electrical Safety Training
1. Prevention of Electrical Hazards
Effective electrical safety training is crucial in preventing electrical hazards. Training provides workers with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and mitigate electrical risks. It also promotes safe work practices, reducing the likelihood of incidents.

2. Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with electrical safety regulations is mandatory to ensure a safe working environment. Electrical safety training ensures that employees understand and adhere to these regulations, minimizing the risk of legal penalties.
3. Enhancing Workplace Safety Culture
Integrating electrical safety training with other safety programs, such as fall protection courses and first aid training courses in Surrey, fosters a comprehensive safety culture within the workplace. This holistic approach to safety encourages employees to prioritize their well-being and that of their colleagues.
Comprehensive Electrical Safety Training Programs
Core Components of Electrical Safety Training
- Hazard Identification: Training employees to recognize and assess electrical hazards in the workplace.
- Safe Work Practices: Teaching safe work practices, including lockout/tagout procedures, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and safe handling of electrical equipment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring employees understand and comply with electrical safety regulations and standards.
- Emergency Response: Training employees to respond effectively to electrical emergencies, including administering first aid and using fire extinguishers.
Advanced Electrical Safety Training
- Arc Flash Training: Specialized training on arc flash hazards, including risk assessment, PPE requirements, and safe work practices.
- High Voltage Safety: Training on the safe operation and maintenance of high voltage equipment.
- Electrical Safety Audits: Conducting regular safety audits to identify and rectify potential electrical hazards.
Integrating Electrical Safety with Other Safety Programs
Fall Protection Training
Fall protection training is essential for workers who perform tasks at heights. Integrating fall protection training with electrical safety training ensures that workers are equipped to handle both fall and electrical hazards, reducing the risk of incidents. Fall protection courses provide workers with the knowledge and skills to use fall protection equipment correctly and follow safe work practices.
Confined Space Training in Vancouver
Confined spaces present unique challenges and hazards, including electrical risks. Confined space training in Vancouver educates workers on safe entry and exit procedures, atmospheric testing, and emergency response. By integrating electrical safety training with confined space training, workers are better prepared to handle the specific risks associated with confined spaces.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
First aid training is a critical component of workplace safety. First aid training courses in Surrey teach employees how to respond to medical emergencies, including electrical injuries. Integrating first aid training with electrical safety training ensures that workers are prepared to provide immediate care in the event of an electrical incident.
Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3
Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3 provide comprehensive training on first aid and emergency response. These courses cover a range of medical emergencies, including those resulting from electrical hazards. By incorporating electrical safety into Occupational First Aid courses, workers receive a well-rounded education on workplace safety.
Compliance with Electrical Safety Regulations
Key Electrical Safety Regulations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA):OSHA sets and enforces standards for electrical safety in the workplace. Compliance with OSHA regulations is mandatory to ensure a safe working environment.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA): The CSA develops standards for electrical safety in Canada. Compliance with National Fire Code standardsensures that electrical installations and equipment meet safety requirements.
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): The NFPA provides guidelines for electrical safety, including the NFPA 70E standard for electrical safety in the workplace.
Importance of Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with electrical safety regulations is crucial for preventing incidents and avoiding legal penalties. Electrical safety training programs should emphasize the importance of adhering to these regulations and provide employees with the knowledge and skills to comply with them.
Conducting Safety Audits
Regular safety audits are essential for maintaining compliance with electrical safety regulations. Safety audits identify potential hazards, evaluate the effectiveness of safety measures, and ensure that safety protocols are being followed

Developing an Effective Electrical Safety Program
Assessing Workplace Risks
The first step in developing an effective electrical safety program is to assess the workplace for electrical risks. This involves identifying potential hazards, evaluating the likelihood and severity of incidents, and implementing measures to mitigate these risks.
Implementing Safe Work Practices
Safe work practices are essential for preventing electrical incidents. These practices include:
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Ensuring that electrical equipment is de-energized and isolated before maintenance or repair work is performed. This includes using locks and tags to indicate that the equipment is not to be used until maintenance is complete, preventing accidental energization.
- Use of PPE: Provide employees with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing. Regularly inspecting and replacing PPEensures that it remains effective and reliable. Proper training on the correct use of PPE is crucial to maximize protection against electrical hazards.
- Safe Handling of Electrical Equipment: Training employees on the proper use, maintenance, and inspection of electrical equipment. This includes understanding the equipment’s operating limits, recognizing signs of wear and damage, and knowing how to perform routine inspections. Employees should also be trained to report any equipment defects immediately and follow procedures for safe handling and storage of electrical tools and devices.
Providing Comprehensive Training
Comprehensive electrical safety training is crucial for ensuring that employees are equipped to handle electrical hazards. Training should be provided to all employees, including new hires and those working with electrical equipment.
Conducting Regular Safety Audits
Regular safety audits help identify potential hazards and evaluate the effectiveness of safety measures. Audits should be conducted by qualified personnel and include a thorough review of electrical installations, equipment, and safety protocols.
Promoting a Safety Culture
A strong safety culture is essential for preventing electrical incidents. This involves fostering an environment where safety is prioritized, and employees are encouraged to take proactive measures and trained with OFA, confined space safety, and fall protection courses to protect themselves and their colleagues.
Metro Safety Training offers a wide range of safety training programs designed to meet the needs of businesses across various industries. From electrical safety training to fall protection courses and confined space safety training, Metro Safety Training provides the knowledge and skills necessary to create safer, more productive work environments.
Contact Metro Safety Training today to learn more about our comprehensive training programs and how we can help your business prioritize safety and enhance competitiveness.








