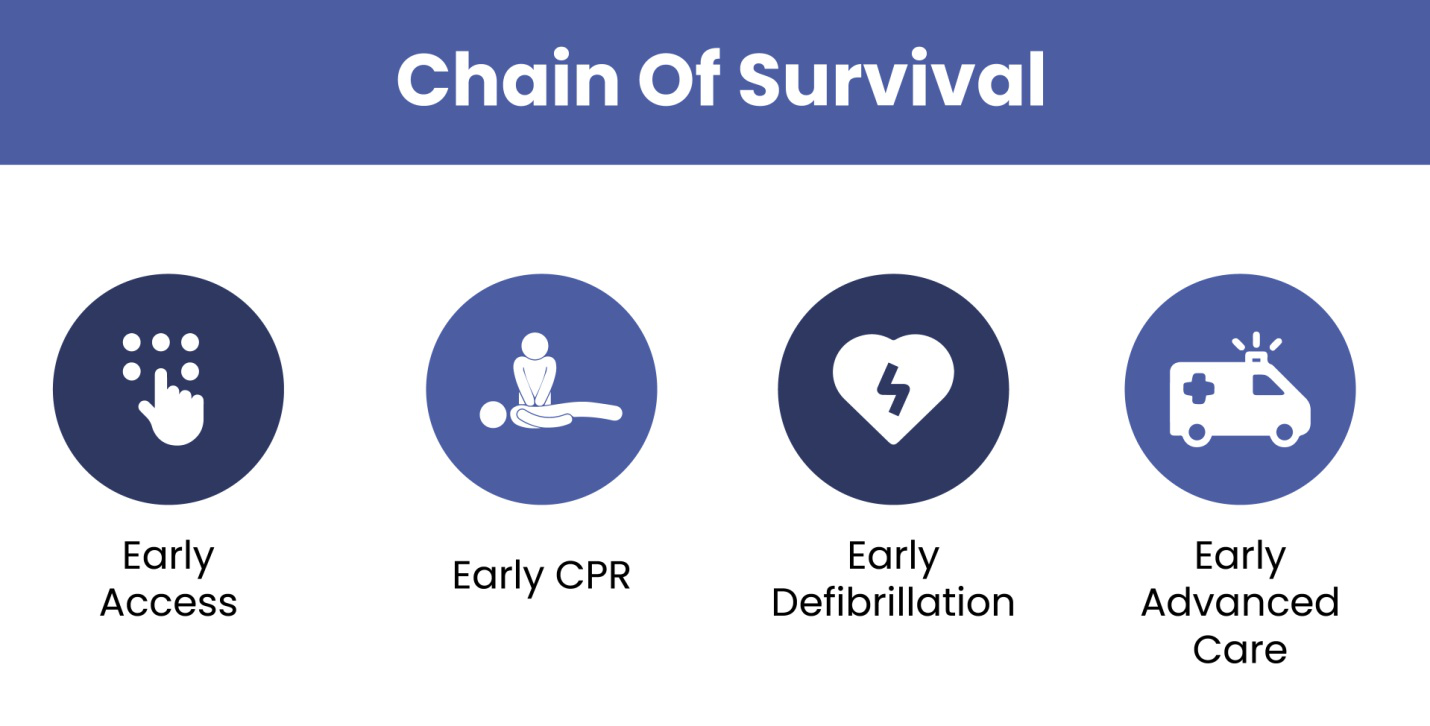
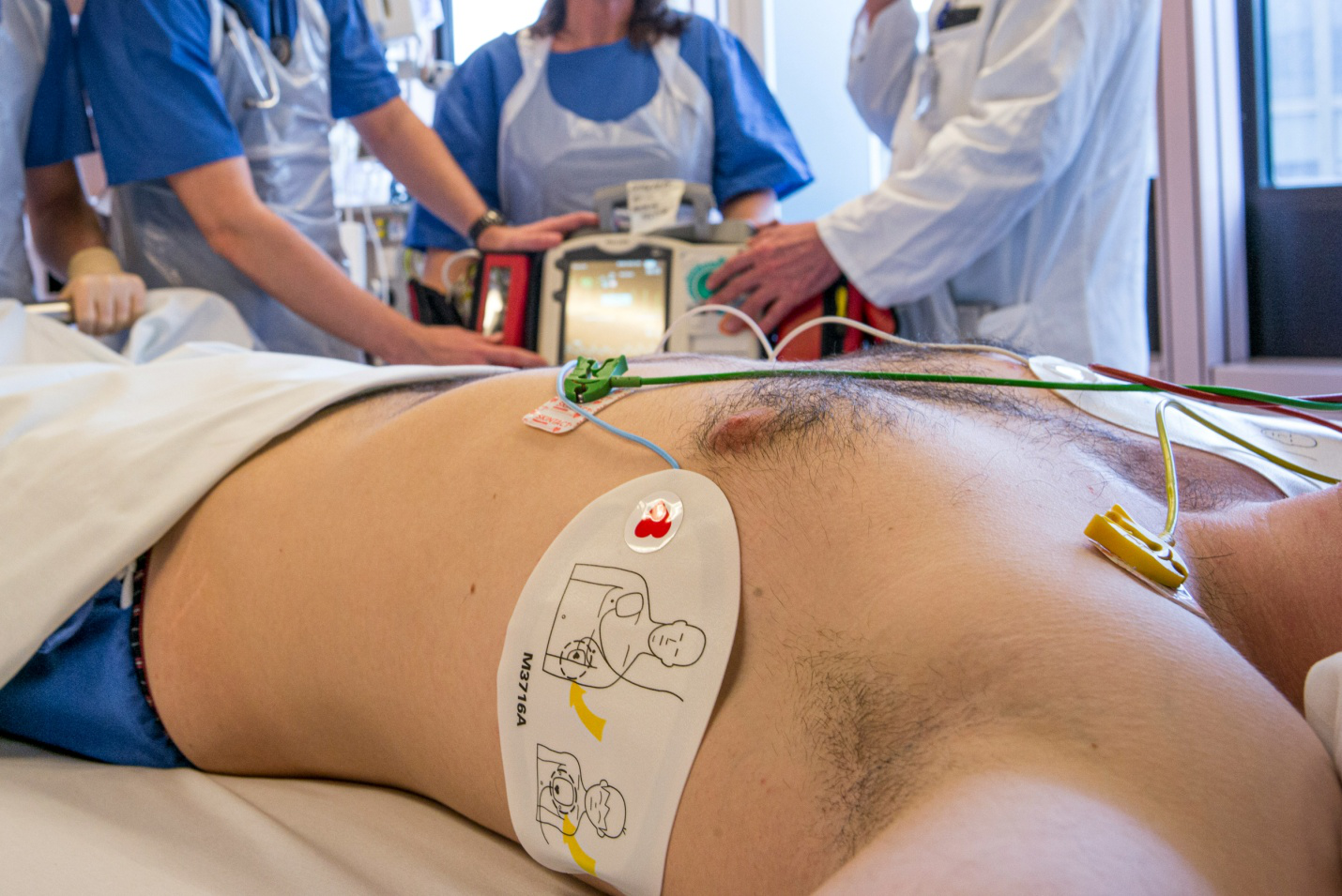
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillator (AED) training are critical life-saving skills that can make the difference between life and death during cardiac emergencies.
In Canada, as in many parts of the world, sudden cardiac arrest is one of the leading causes of death, and immediate intervention significantly improves survival rates. This blog will discuss the importance of CPR-C with AED training and identify key personnel in various workplaces who should receive this training, emphasizing their critical role in emergency response.
Understanding CPR A, B, C, and HCP
Before diving into the specifics of CPR-C with AED training, it’s essential to understand the different levels of CPR training available:
CPR A
CPR Level A is the most basic level, focusing on adult CPR and choking procedures. It’s suitable for the general public who may need to assist in emergencies involving adults.
CPR B
CPR Level B includes everything in CPR A, but it also covers CPR and choking procedures for children and infants. This level is often recommended for parents, caregivers, and those who work with children.
CPR C
CPR Level C encompasses the skills learned in CPR A and B but also includes training on two-rescuer CPR techniques for adults, children, and infants. It’s the most comprehensive level designed for the general public and workplace responders who may need to perform CPR in a team setting.
CPR HCP
CPR HCP (Health Care Provider) is designed for healthcare professionals and includes advanced techniques and scenarios they might encounter in their work environment. It involves more detailed training on how to use AEDs, manage airways, and other advanced skills.
What’s CPR-C with AED Training
CPR-C with AED training is a comprehensive course that equips participants with the knowledge and skills to perform CPR on adults, children, and infants and to use an AED effectively.
AEDs are devices that can analyze heart rhythms and, if necessary, deliver an electrical shock to help the heart re-establish an effective rhythm.
News report that a Canadian suffers from cardiac arrest every 9 minutes. The CPR-C with AED training ensures that individuals are prepared to act swiftly and effectively in these emergencies, significantly improving the chances of survival for the victim.
Key Components of CPR-C with AED Training:
- Recognition of Cardiac Arrest: Identifying signs of cardiac arrest promptly is crucial for effective intervention.
- Chest Compressions: Learning proper hand placement, compression depth, and rate for different age groups.
- Rescue Breaths: Techniques for providing effective breaths using mouth-to-mouth or barrier devices.
- AED Use: Understanding how to operate an AED, including attaching pads, following voice prompts, and ensuring safety during shock delivery.
- Two-Rescuer CPR: Coordination and communication strategies for performing CPR with another rescuer.
- Dealing with Choking: Procedures for relieving choking in adults, children, and infants.
Employees Who Can Benefit from CPR-C with AED Training
News report that a Canadian suffers from cardiac arrest every 9 minutes. The CPR-C with AED training ensures that individuals are prepared to act swiftly and effectively in these emergencies, significantly improving the chances of survival for the victim.
Certain key personnel across all sectors can benefit immensely from CPR-C with AED training. Here are some detailed examples:
1. Security Personnel
Security guards are often the first point of contact in many emergencies. They patrol the premises, monitor safety systems, and are frequently on-site during business hours. Equipping them with CPR-C and AED training ensures they can provide immediate assistance before medical professionals arrive, particularly in high-traffic areas such as malls, office buildings, and event venues.
Their training can make a critical difference during the first few minutes of a cardiac emergency, which is vital for survival.
2. Health and Safety Officers
These individuals are responsible for maintaining a safe working environment and implementing safety protocols. With CPR-C and AED training, they can respond effectively to cardiac emergencies, ensuring the safety of employees and visitors. Health and safety officers are often tasked with emergency preparedness, and having advanced life-saving skills enhances their ability to manage emergencies comprehensively.
3. Construction Workers
The physically demanding and hazardous nature of construction work makes the risk of cardiac events higher. Training key personnel on-site can lead to quicker response times and better outcomes during emergencies. Construction sites often have limited access to immediate medical help, so having trained individuals on-site can provide critical early intervention, significantly improving the chances of survival until emergency medical services arrive.
4. Manufacturing and Industrial Workers
Similar to construction, these environments can be high-stress and physically taxing. Employees working with heavy machinery or in high-stakes production lines may experience elevated heart rates and stress levels. Having trained employees can mitigate the risks associated with cardiac incidents.
Furthermore, industrial settings often involve loud machinery, and trained workers can quickly recognize and respond to emergencies that might go unnoticed in a noisy environment.
5. Retail and Hospitality Staff
Employees in malls, hotels, restaurants, and other public spaces encounter large numbers of people daily. Training them in CPR-C with AED prepares them to handle emergencies in these crowded settings. In large retail environments, the immediate availability of trained staff can prevent tragic outcomes, especially in areas with significant foot traffic where waiting for paramedics might take too long.
6. Transportation Workers
Bus drivers, airline staff, and other transportation workers are responsible for the safety of many passengers. CPR-C and AED training enables them to manage emergencies effectively, potentially saving lives while awaiting professional help. For instance, flight attendants can provide life-saving care during flights, where immediate medical help is not available, ensuring passengers receive the best possible care until the plane lands.
7. Teachers and School Staff
Children are not immune to cardiac emergencies, and having trained personnel in schools can make a significant difference. Teachers, administrators, and support staff with CPR-C and AED training are essential for creating a safer learning environment. Schools are places where large groups gather, and having multiple trained individuals ensures that help is always nearby, whether in classrooms, sports fields, or cafeterias.
8. Human Resources and Management Teams
HR professionals and managers play a crucial role in workplace well-being. Training these individuals ensures they are prepared to handle emergencies, fostering a culture of safety within the organization. Management teams often set the tone for workplace policies, and their commitment to safety through CPR-C and AED training underscores the organization’s dedication to employee health.
9. Employee Health and Wellness Coordinators
These roles are increasingly common in large corporations. Equipped with CPR-C and AED training, they can lead health initiatives and respond effectively during medical emergencies. Wellness coordinators are often involved in planning health and safety drills, and their advanced training ensures that they can guide others during actual emergencies.
10. Fitness Trainers and Gym Staff
Gyms and fitness centers are places where physical exertion is high, increasing the likelihood of cardiac events. Trained staff can provide immediate assistance, improving the chances of survival. Fitness environments attract individuals of all ages and fitness levels, and the ability to respond to emergencies swiftly can reassure members and potentially save lives.
11. Lifeguards and Pool Attendants
Water-related activities carry inherent risks. Lifeguards with CPR-C and AED training are vital in responding to drowning incidents and other emergencies in aquatic environments. Pools and beaches often have large crowds, and the prompt response of trained lifeguards can prevent drowning fatalities and provide critical care until emergency services arrive.
12. Caregivers and Home Support Workers
Those who care for the elderly or individuals with medical conditions are often in situations where cardiac emergencies can occur. Training ensures they can provide immediate care, improving outcomes for those they support. Home caregivers frequently work in isolated settings, making their ability to perform CPR and use an AED crucial until professional help can take over.
13. Wildlife and Park Rangers
These roles often involve working in remote areas where emergency services might take longer to reach. Having CPR-C and AED training enables them to respond effectively in case of emergencies. Rangers frequently interact with the public and face situations where medical emergencies can arise, such as during hikes, wildlife encounters, or natural disasters.
The value of CPR-C with AED training lies in its potential to save lives, and ensuring that those most likely to encounter emergencies are well-equipped with these skills is a critical step towards a safer, healthier society.
Metro Safety Training provides CPR-C with AED training courses tailored for employees in British Columbia workplaces. We also offer Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3 courses to empower your workforce with basic first-aid skills particularly useful in BC workplaces.
If you want to ensure your team is equipped with life-saving skills, consider contacting us today and let our experts work their magic!