Promoting a safety culture within the workplace is crucial for reducing accidents, enhancing employee well-being, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Leadership is pivotal in cultivating this culture by setting standards, modeling behaviors, and implementing effective training programs.
This blog explores the role of leadership in promoting a safety culture, highlights training programs for safety leaders, and examines their impact on overall workplace safety.
What is Safety Culture?
Safety culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and practices regarding safety within an organization. The collective attitude towards safety influences how employees perceive and respond to safety issues. A strong safety culture prioritizes safety at all levels, from leadership to frontline workers, and integrates safety into every aspect of operations.
Components of Safety Culture
Leadership Commitment:
- Leaders must demonstrate a genuine commitment to safety, setting the tone for the entire organization.
- Safety should be a core value, reflected in policies, procedures, and actions.
Employee Involvement:
- Engaging employees in safety initiatives fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Encouraging open communication and feedback helps identify and address safety concerns.
Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly reviewing and improving safety practices ensures they remain effective and relevant.
- Implementing lessons learned from incidentsand near-misses helps prevent future occurrences.
Training and Education:
- Comprehensive training programs equip employees with the knowledge and skills to work safely.
- Specialized training, such as and confined space training in Vancouver, addresses specific hazards.
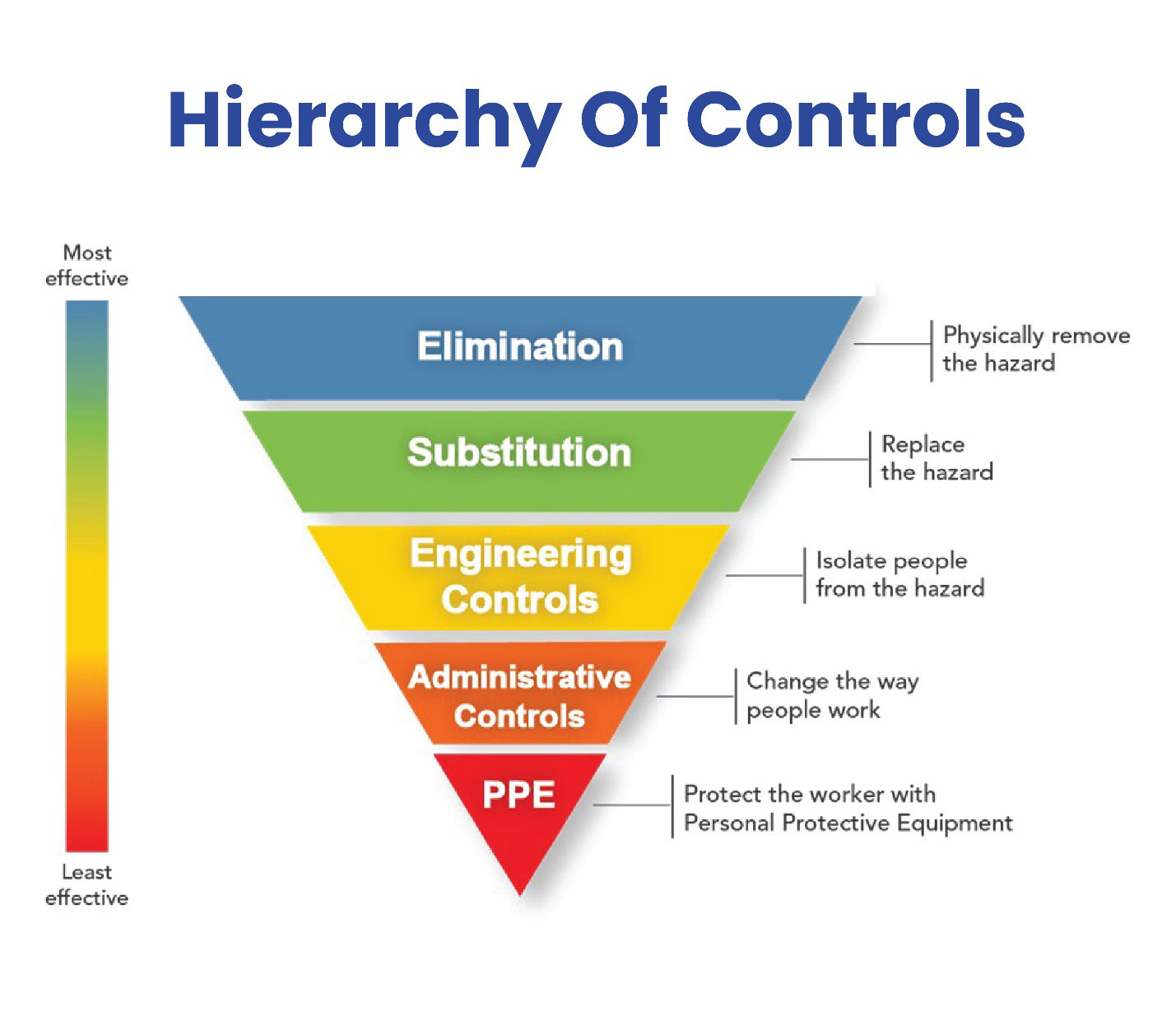
Importance of Safety Culture
A strong safety culture offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Accidents and Injuries:A proactive approach to safety minimizes the risk of workplace incidents.
- Increased Productivity:A safe work environment enhances employee morale and efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance:Adhering to safety standards ensures compliance with legal requirements.
- Positive Reputation:Companies known for their commitment to safety attract top talent and clients.
The Role of Leadership in Promoting Safety Culture
Leadership Commitment to Safety
Effective safety leadership starts with a genuine commitment to safety. Leaders must prioritize safety as a core value and demonstrate this commitment through their actions and decisions.
Setting the Vision:
- Leaders should articulate a clear vision for safety, outlining expectations and goals.
- Communicating the importance of safety at all levels reinforces its significance.
Leading by Example:
- Leaders must model safe behaviors and practices, setting a standard for others to follow.
- Participating in safety training programs, such as first aid training courses in Surrey, showcases their dedication.
Allocating Resources:
- Investing in safety programs, equipment, and training demonstrates a commitment to safety.
- Providing resources for Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3ensures employees are prepared for emergencies.
Building a Safety Leadership Team
Developing a team of safety leaders is crucial for embedding safety into the organizational culture. These leaders play a key role in implementing and sustaining safety initiatives.
Identifying Safety Champions:
- Select individuals who are passionate about safety and possess strong leadership qualities.
- Encourage participation in specialized training, such as confined space training in Vancouver.
Providing Leadership Training:
- Offer leadership development programs focused on safety management and communication.
- Training should cover risk assessment, incident investigation, and emergency response.
Empowering Leaders:
- Give safety leaders the authority and resources to make decisions and implement changes.
- Encourage them to lead safety meetings, conduct inspections, and mentor colleagues.
Communication and Engagement
Effective communication and engagement are vital for promoting a safety culture. Leaders must foster an environment where safety is openly discussed and valued.
Open Communication:
- Create channels for employees to report safety concerns and share ideas.
- Regularly communicate safety updates, policies, and success stories.
Employee Involvement:
- Involve employees in safety committees, inspections, and training sessions.
- Encourage participation in safety programs, such as Standard first aid,and Emergency First Aid, and CPR.
Recognition and Rewards:
- Recognize and reward individuals and teams for their contributions to safety.
- Celebrating safety achievements reinforces positive behaviors and motivates others.
Training Programs for Safety Leaders
Importance of Safety Training
Safety training is essential for equipping leaders with the knowledge and skills to manage and promote safety effectively. Comprehensive training programs address various aspects of safety management, from hazard identification to emergency response.
Fall Protection Training
Fall protection training is crucial for preventing falls, one of the leading causes of workplace injuries and fatalities. This training equips safety leaders with the knowledge to identify fall hazards and implement preventive measures.
- Risk Assessment:
- Teach leaders how to conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential fall hazards.
- Emphasize the importance of regular inspections and maintenance.
- Fall Prevention Strategies:
- Provide training on the use of fall protection equipment, such as harnesses and guardrails.
- Highlight best practices for working at heights safely.
- Emergency Response:
- Train leaders on responding to fall incidents, including first aid and rescue techniques.
- Ensure they understand the importance of timely and effective intervention.
Confined Space Training in Vancouver
Confined space training in Vancouver prepares safety leaders to manage the unique hazards associated with confined spaces. This training is essential for industries such as construction, manufacturing, and utilities.
- Hazard Identification:
- Teach leaders to recognize and assess the hazards associated with confined spaces.
- Cover atmospheric hazards, physical hazards, and engulfment risks.
- Entry Procedures:
- Provide training on safe entry and exit procedures for confined spaces.
- Emphasize the importance of permits, monitoring, and communication.
- Emergency Response:
- Train leaders on emergency response protocols for confined space incidents.
- Ensure they are equipped to conduct rescues and administer first aid.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
First aid training courses in Surrey are essential for safety leaders, equipping them with the skills to respond to medical emergencies. This training is crucial for managing injuries and illnesses in the workplace.
- Basic First Aid:
- Cover fundamental first aid skills, such as wound care, CPR, and AED use.
- Emphasize the importance of timely intervention and stabilization.
- Advanced First Aid:
- Provide more in-depth training on managing severe injuries and medical conditions.
- Include scenarios and hands-on practice to build confidence and competence.
- Emergency Planning:
- Train leaders on developing and implementing emergency response plans.
- Highlight the importance of coordination with emergency services.
Impact of Safety Leadership on Workplace Safety
Reduced Accidents and Injuries
Effective safety leadership significantly reduces the incidence of workplace accidents and injuries. By promoting a safety culture and implementing robust safety programs, leaders create a safer work environment.
Proactive Hazard Identification:
- Leaders trained in risk assessment and hazard identification can proactively address potential risks.
- Regular inspections and audits help identify and mitigate hazards before they cause harm.
Improved Safety Practices:
- Training programs such as fall protection trainingand confined space training in Vancouver equip leaders with the knowledge to implement effective safety practices.
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations reduces the likelihood of incidents.
Timely Emergency Response:
- Leaders trained in first aid training courses in Surreyand Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3 can respond promptly and effectively to emergencies.
- Timely intervention and care minimize the severity of injuries and improve outcomes.
Regulatory Compliance
Safety leadership ensures compliance with safety regulations and standards, avoiding legal and financial penalties.
Understanding Regulations:
- Leaders trained in safety managementare knowledgeable about relevant safety regulations and standards.
- Ensuring compliance with regulations such as Occupational First Aid courses in BCprotects the organization from legal liabilities.
Implementing Best Practices:
- Safety leaders implement industry best practices to maintain high safety standards.
- Continuous improvement and adherence to regulations ensure ongoing compliance.
Documenting and Reporting:
- Effective safety leadership includes thorough documentation and reporting of safety practices and incidents.
- Accurate records demonstrate compliance and support continuous improvement efforts.
Elevate your organization’s safety standards with Metro Safety Training. Our specialized courses, including fall protection training, confined space training in Vancouver, and first aid training courses in Surrey, are designed to empower your leaders and workforce with the skills necessary to maintain a safe and compliant workplace. Enroll in our Occupational First Aid Levels 1, 2, and 3, Standard First Aid, and Emergency First Aid and CPR programs to ensure your team is prepared for any emergency.
Contact Metro Safety Training today to build a stronger safety culture and protect your most valuable asset—your employees.









