Ensuring safety in construction is paramount, and scaffolding safety plays a critical role in protecting workers from falls and injuries. Comprehensive scaffolding safety training is essential to minimize risks, comply with regulations, and foster a culture of safety on construction sites. This blog explores the importance of scaffolding safety, effective training methods, inspection procedures, and compliance with scaffolding regulations.
The Importance of Scaffolding Safety
Scaffolding is a common feature on construction sites, providing workers with access to elevated areas. However, scaffolding-related accidents are a leading cause of falls and injuries in construction. Ensuring scaffolding safety through rigorous training and adherence to regulations can significantly reduce these risks.
The Risks of Scaffolding
- Falls from Heights:The primary hazard of scaffolding is the risk of falling from significant heights, leading to severe injuries or fatalities.
- Structural Failures:Poorly constructed or maintained scaffolds can collapse, posing a risk to workers on and around the scaffold.
- Falling Objects:Tools, materials, and debris falling from scaffolds can injure workers below.
- Electrical Hazards:Scaffolds erected near power lines pose a risk of electrocution.
Check out our first-aid training courses for employees in Surrey.
Comprehensive Scaffolding Safety Training
Effective scaffolding safety training is vital for ensuring that workers understand how to set up, use, and dismantle scaffolding safely. Training should cover the following key areas:
Understanding Scaffolding Components
Training should start with a thorough understanding of the different components of scaffolding, including:
- Standards:Vertical tubes that support the scaffold structure.
- Ledgers:Horizontal tubes that connect the standards.
- Transoms:Horizontal tubes that support the decking.
- Decking:Platforms where workers stand.
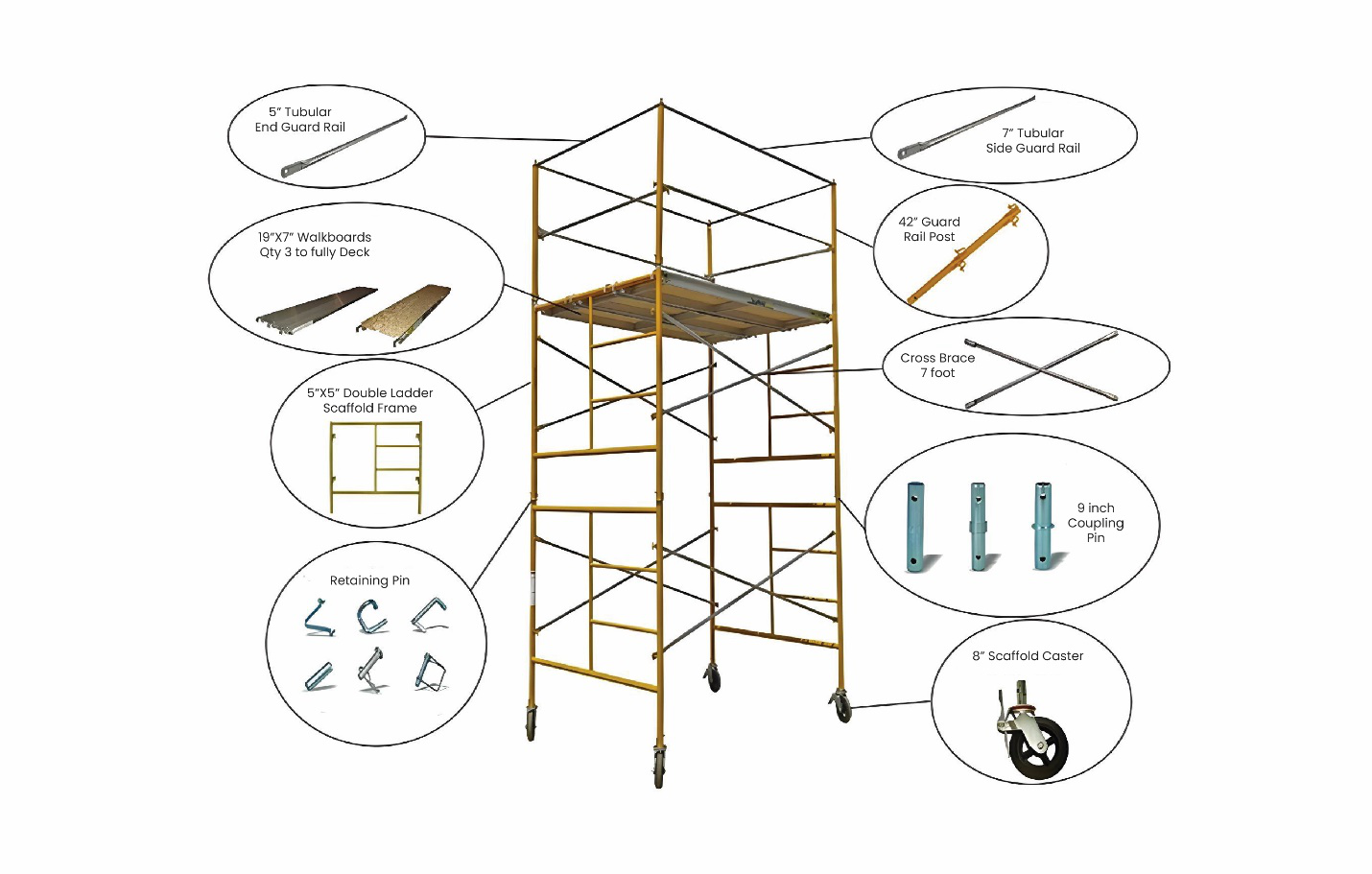
- Bracing:Diagonal tubes that provide stability.
Proper Erection and Dismantling Procedures
Workers should be trained on the correct procedures for erecting and dismantling scaffolds, including:
- Foundation Preparation:Ensuring the ground is stable and capable of supporting the scaffold.
- Scaffold Erection:Step-by-step procedures for setting up the scaffold, ensuring stability and proper alignment.
- Scaffold Dismantling:Safe methods for taking down the scaffold, ensuring that workers are not exposed to fall hazards.
Fall Protection Measures
Training should emphasize the importance of fall protection measures, such as:
- Guardrails:Installing guardrails on all open sides and ends of scaffolds.
- Toe Boards:Using toe boards to prevent tools and materials from falling.
- Personal Fall Arrest Systems:Proper use of harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points.
Load Capacity and Stability
Workers should be trained on the importance of maintaining scaffold stability and not exceeding load capacities. This includes understanding:
- Maximum Load Ratings:Adhering to the manufacturer’s load ratings for the scaffold.
- Even Load Distribution:Ensuring loads are evenly distributed across the scaffold platform.
- Avoiding Overloading:Not placing excessive materials or tools on the scaffold.
Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of scaffolding are crucial for ensuring safety. Training should cover:
- Pre-Use Inspections:Conduct thorough inspections before each use to identify defects or damage.
- Periodic Inspections:Regularly inspecting scaffolds during use to ensure ongoing safety.
- Maintenance Procedures:Proper methods for repairing or replacing damaged components.
Hazard Awareness
Training should include awareness of potential hazards related to scaffolding, such as:
- Weather Conditions:Understanding how weather conditions like wind, rain, and ice can affect scaffold safety.
- Nearby Activities:Being aware of activities around the scaffold that could pose risks, such as moving machinery or other construction work.
Scaffolding Inspection Procedures
Regular inspections are critical to maintaining scaffold safety, and they should be conducted by a competent person and follow a systematic approach.
1. Pre-Erection Inspection
Before erecting the scaffold, inspect the following:
- Ground Conditions:Ensure the ground is stable and free from debris.
- Scaffold Components:Check for any damaged or missing components.
- Environmental Hazards:Identify any nearby hazards, such as power lines or moving machinery.
2. Erection Inspection
During scaffold erection, inspect the following:
- Foundation:Ensure the scaffold is erected on a stable foundation.
- Structural Integrity:Check that all components are securely connected and properly aligned.
- Guardrails and Toe Boards:Ensure guardrails and toe boards are installed correctly.
3. Daily Inspections
Conduct daily inspections before each use:
- Structural Stability:Check for any signs of instability or damage.
- Guardrails and Toe Boards:Ensure these are in place and secure.
- Load Capacity:Verify that the scaffold is not overloaded.
Train your workers with standard and emergency first aid courses along with fall protection and confined space safety programs for maximum hazard prevention.
4. Periodic Inspections
Conduct periodic inspections during use:
- Weather Conditions:Assess how weather conditions may affect scaffold safety.
- Wear and Tear:Look for signs of wear and tear on scaffold components.
- Worker Behavior:Monitor workers to ensure they are using the scaffold correctly.
5. Post-Use Inspections
After dismantling the scaffold, inspect the following:
- Component Condition:Check for any damage to scaffold components.
- Storage:Ensure components are stored properly to prevent damage.
Compliance with Scaffolding Regulations
Compliance with scaffolding regulations is essential for ensuring safety and avoiding legal consequences. Key regulations and standards include:
1. WorkSafeBC Regulations
WorkSafeBC sets stringent regulations for scaffold safety in British Columbia, aiming to protect workers from potential hazards associated with scaffolding. Key requirements include:
- General Requirements:Ensuring scaffolds are capable of supporting their weight and at least four times the maximum intended load. This includes the careful selection of materials and construction practices to ensure stability and safety.
- Access and Egress:Providing safe access to and from scaffolds, which involves the use of ladders, ramps, or stair towers that comply with safety standards. This is crucial for preventing falls and facilitating the safe movement of workers.
- Fall Protection:Using guardrails, toe boards, and personal fall arrest systems to prevent falls. Workers must undergo fall protection training in BC to understand the proper use and maintenance of these systems. This training is vital for ensuring that all personnel are aware of the risks and the necessary precautions.
- Training:Ensuring workers receive adequate training on scaffold safety, which covers the correct assembly, inspection, and use of scaffolds. This training should also include emergency procedures and rescue plans in case of accidents. Additionally, workers involved in scaffold assembly and use should be familiar with confined space safety protocols if they encounter such environments.
2. CSA Standards
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) provides comprehensive standards for scaffold safety, ensuring that scaffolding practices across Canada meet high safety requirements. Key standards include:
- CSA S269.2:Access Scaffolding for Construction Purposes, which outlines the design, erection, use, and dismantling of scaffolding systems. This standard ensures that scaffolds are constructed and maintained to support loads safely and provide a stable work platform.
- CSA Z797:Code of Practice for Access Scaffold, which offers guidelines for the safe use of scaffolding, including recommendations for proper access, guardrails, and fall protection measures. This code of practice is essential for maintaining consistent safety practices across different worksites.
- CSA Z259 Series:Standards for fall protection systems and equipment used in conjunction with scaffolding. This includes harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points, which are critical components of a comprehensive fall protection plan. Workers should also receive forklift operator training in Vancouver if they are using forklifts to transport scaffolding materials, ensuring safe handling and operation.
These regulations and standards ensure that scaffolding practices in Canada are designed to protect workers effectively. Compliance with these guidelines helps prevent falls and injuries, promoting a safer working environment. Proper training, including fall protection training in BC, confined space safety, and forklift operator training in Vancouver, is essential to equip workers with the knowledge and skills needed to adhere to these safety standards.
3. Local Regulations
Local regulations may also apply, depending on the location of the construction site. It is essential to be familiar with and comply with these regulations.
Ensuring Effective Scaffolding Safety Training
To ensure effective scaffolding safety training, follow these best practices:
· Qualified Instructors
Use qualified instructors with extensive experience in scaffold safety to conduct training sessions. Instructors should be knowledgeable about current regulations and best practices.
· Hands-On Training
Incorporate hands-on training to allow workers to practice erecting, using, and dismantling scaffolds under supervision. Practical experience is crucial for reinforcing theoretical knowledge.
· Regular Refresher Courses
Offer regular refresher courses to keep workers updated on the latest safety standards and practices. Refresher courses help reinforce knowledge and address any changes in regulations.
· Tailored Training Programs
Tailor training programs to the specific needs of the construction site and the types of scaffolds used. Customized training ensures relevance and effectiveness.
· Comprehensive Training Materials
Provide comprehensive training materials, including manuals, videos, and interactive modules. These materials serve as valuable references for workers.
· Assessments and Evaluations
Conduct assessments and evaluations to measure the effectiveness of training programs. Use quizzes, practical tests, and feedback to identify areas for improvement.
At Metro Safety Training, our expert-led courses cover a wide range of safety topics, including fall protection training, confined space training in Vancouver, and first aid training courses in Surrey. Equip your team with the necessary tools to stay safe and compliant on construction sites. Call us now for more information.









