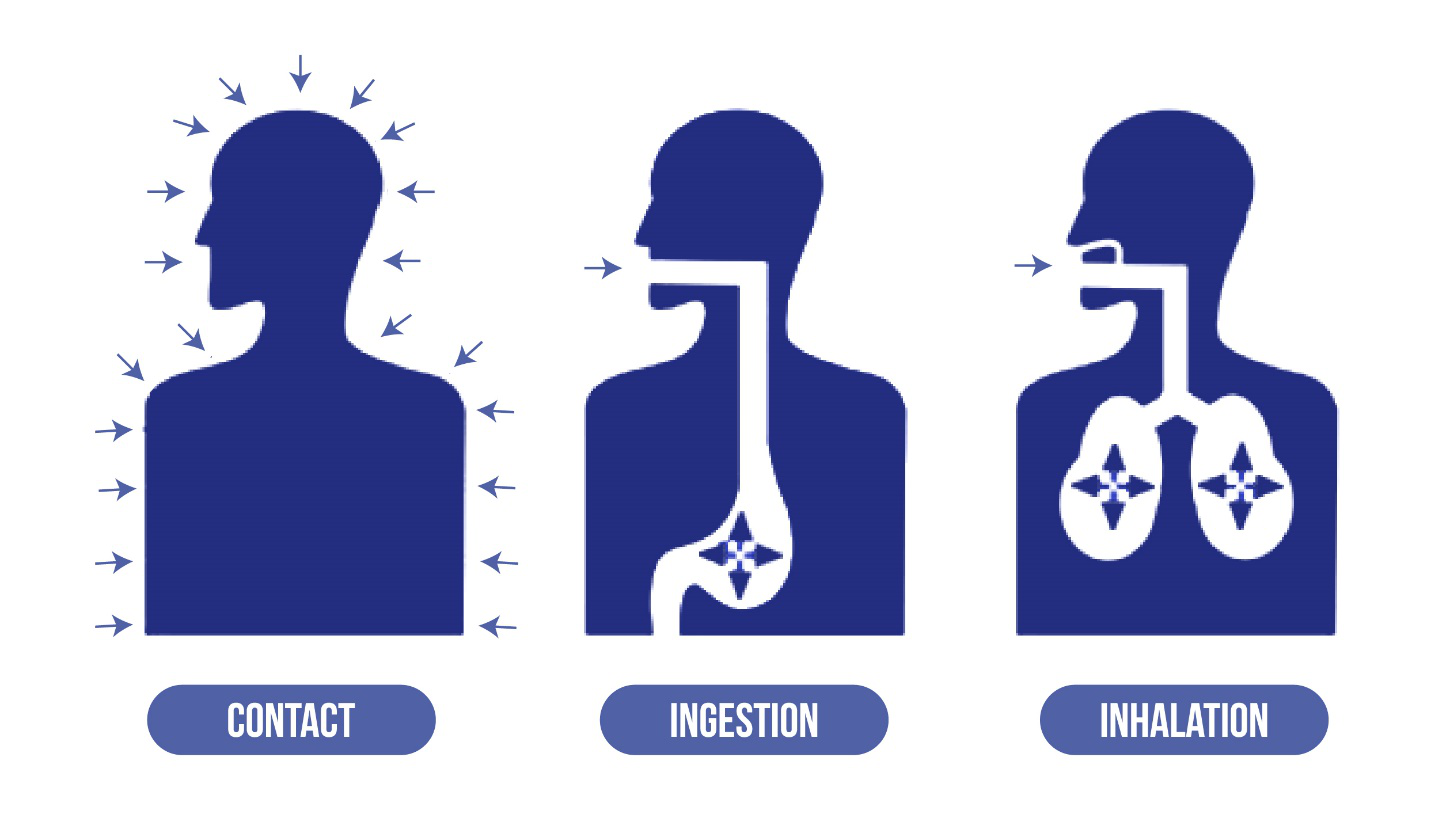
Hazardous materials, particularly lead, and asbestos, pose significant health risks in various workplaces. Effective training for the safe handling and removal of these materials is crucial to protecting workers and ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines.
This blog will discuss the dangers of lead and asbestos exposure, outline the regulatory framework governing their management, and highlight the comprehensive training programs available for safe handling and removal. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of integrating fall protection training, confined space safety training, and first aid training courses in Surrey to enhance overall workplace safety.
Understanding the Dangers of Lead and Asbestos Exposure
The Health Risks of Lead Exposure
Lead is a toxic metal that can cause severe health issues when ingested or inhaled. The dangers of lead exposure include:
- Neurological Effects:Lead can damage the nervous system, leading to cognitive impairments, behavioral changes, and decreased IQ, particularly in children.
- Cardiovascular Issues:Prolonged lead exposure can increase blood pressure and the risk of heart disease.
- Renal Damage:Lead can accumulate in the kidneys, causing chronic kidney disease.
- Reproductive Problems:Lead exposure can lead to infertility, miscarriages, and developmental issues in fetuses.
The Health Risks of Asbestos Exposure
Asbestos, a group of naturally occurring fibrous minerals, has been widely used in construction and manufacturing. However, asbestos exposure can cause serious health problems, including:
- Asbestosis:A chronic lung condition caused by inhaling asbestos fibers, leading to scarring of lung tissue and breathing difficulties.
- Mesothelioma:A rare and aggressive cancer affecting the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart, primarily caused by asbestos exposure.
- Lung Cancer:Asbestos exposure significantly increases the risk of lung cancer, especially in smokers.
- Pleural Diseases:These include pleural plaques, pleural effusions, and diffuse pleural thickening, which affect the lining of the lungs and chest cavity.
Regulatory Guidelines for Handling Hazardous Materials
Canada’s Occupational Health and Safety Regulations
In Canada, the handling of hazardous materials such as lead and asbestos is governed by strict regulations to protect workers’ health and safety. Key regulatory guidelines include:
- Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS):WHMIS provides a comprehensive system for classifying hazardous materials, labeling containers, and providing safety data sheets (SDS) and worker education programs.
- Provincial and Territorial Regulations:Each province and territory in Canada has its own specific regulations and guidelines for handling hazardous materials, including lead and asbestos.
Guidelines for Lead Handling and Removal
- Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs):Regulatory agencies set permissible exposure limits for lead in the workplace air to minimize workers’ risk.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Workers handling lead must wear appropriate PPE, including respirators, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Engineering Controls:Use of ventilation systems, dust suppression techniques, and containment measures to reduce lead exposure.
- Safe Work Practices:Implementing procedures for safe handling, storage, and disposal of lead-containing materials.
Guidelines for Asbestos Handling and Removal
- Asbestos Abatement Regulations:These regulations outline the procedures for the safe removal, encapsulation, and enclosure of asbestos-containing materials.
- Training and Certification:Workers involved in asbestos abatement must complete specialized training and obtain certification.
- Medical Surveillance:Regular health monitoring of workers exposed to asbestos to detect any early signs of asbestos-related diseases.
- Air Monitoring:Conducting air sampling to ensure asbestos fiber concentrations are within permissible limits during abatement activities.
Comprehensive Training Programs for Safe Handling and Removal
Hazardous Materials Training
To ensure safe handling and removal of hazardous materials, comprehensive training programs are essential. These programs should cover:
- Hazard Recognition:Identifying hazardous materials and understanding their health risks.
- Regulatory Compliance:Familiarity with relevant regulations and guidelines for handling hazardous materials.
- Safe Work Procedures:Implementing safe work practices and using appropriate PPE and engineering controls.
- Emergency Response:Preparing for and responding to incidents involving hazardous materials, including spill containment and cleanup.
Fall Protection Training
Fall protection training is crucial for workers handling hazardous materials at heights. This training includes:
- Identifying Fall Hazards:Recognizing potential fall hazards in the workplace and assessing risks.
- Fall Protection Equipment:Proper use of fall protection equipment, such as harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points.
- Safe Work Practices:Implementing safe practices to prevent falls, including maintaining three points of contact and using guardrails.
- Emergency Procedures:Responding to fall incidents and performing rescue operations.
Confined Space Safety Training
Confined space safety training is essential for workers who may need to enter confined spaces while handling hazardous materials. This training includes:
- Hazard Identification:Recognizing and assessing hazards associated with confined spaces, such as toxic atmospheres and physical hazards.
- Entry Procedures:Implementing safe entry procedures, including using entry permits, conducting atmospheric testing, and ensuring ventilation.
- Rescue Operations:Preparing for and performing confined space rescues, including using appropriate rescue equipment and techniques.
First Aid Training Courses in Surrey
First aid training courses in Surrey provide workers with the knowledge and skills needed to respond to medical emergencies. These courses include:
- Occupational First Aid Level 1:Basic first aid training for workers in low-risk environments, covering CPR, AED use, and treating minor injuries.
- Occupational First Aid Level 2:Advanced first aid training for workers in medium-risk environments, covering primary and secondary assessments, and managing medical emergencies.
- Occupational First Aid Level 3:Comprehensive first aid training for workers in high-risk environments, covering thorough patient assessments, advanced medical care, and managing complex emergencies.
- Occupational First Aid Level 3 Pro Renewal:Refresher training for workers renewing their Level 3 certification, reviewing and updating first aid knowledge and skills.
Developing a Comprehensive Training Program
To develop a comprehensive training program that integrates hazardous materials, fall protection, and confined space safety training, consider the following steps:
- Needs Assessment:Identify the specific training needs of your workforce based on the hazards present in your workplace.
- Course Development:Develop training courses that cover hazardous materials handling, fall protection, confined space safety, and first aid.
- Training Delivery:Deliver training through a combination of classroom instruction, hands-on practice, and simulations.
- Evaluation and Improvement:Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your training program and make improvements based on feedback and incident reports.
The Role of Employers in Ensuring Safe Handling of Hazardous Materials
Providing Adequate Training
Employers are responsible for providing adequate training to workers handling hazardous materials. This includes:
- Initial Training:Providing comprehensive initial training to new workers and those newly assigned to tasks involving hazardous materials.
- Refresher Training:Offering regular refresher training to ensure workers stay up-to-date with the latest safety practices and regulatory requirements.
- Specialized Training:Providing specialized training for specific tasks, such as asbestos abatement or lead removal, and workers in high-risk environments.
Implementing Safe Work Practices
Employers must implement safe work practices to minimize the risks associated with hazardous materials. This includes:
- Developing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):Creating SOPs for tasks involving hazardous materials, including handling, storage, and disposal.
- Using Engineering Controls:Implementing engineering controls, such as ventilation systems and containment measures, to reduce exposure to hazardous materials.
- Providing PPE:Ensuring workers have access to and use appropriate PPE for tasks involving hazardous materials.
Conducting Regular Inspections and Audits
Regular inspections and audits help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Employers should:
- Conduct Workplace Inspections:Regularly inspect work areas for hazards related to hazardous materials, fall protection, and confined spaces.
- Perform Safety Audits:Conduct comprehensive safety audits to assess the effectiveness of safety programs and identify areas for improvement.
- Address Identified Hazards:Take prompt action to address identified hazards and implement corrective measures.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Hazardous Materials Training
Case Study 1: Lead Removal in Construction
A construction company in Vancouver implemented a comprehensive hazardous materials training program for lead removal. The program included:

- Lead Hazard Recognition:Training workers to identify lead hazards and understand the health risks.
- Safe Work Practices:Implementing safe work practices, such as using HEPA-filtered vacuums and wet methods for dust control.
- PPE Use:Providing workers with appropriate PPE, including respirators and protective clothing.
- Regular Monitoring:Conducting regular air monitoring to ensure lead levels remain within permissible limits.
As a result, the company significantly reduced lead exposure incidents and improved overall workplace safety.
Case Study 2: Asbestos Abatement in Industrial Facilities
An industrial facility in Surrey implemented an asbestos abatement training program for workers. The program included:
- Asbestos Hazard Identification:Training workers to recognize asbestos-containing materials and understand the associated health risks.
- Abatement Procedures:Implementing safe asbestos abatement procedures, such as encapsulation and enclosure.
- Certification:Ensuring workers obtained the necessary certification for asbestos abatement.
- Medical Surveillance:Providing regular health monitoring for workers involved in asbestos abatement.
The facility successfully reduced asbestos exposure incidents and maintained compliance with regulatory requirements.
Metro Safety Training offers a wide range of training programs to help employers and workers safely handle hazardous materials and enhance overall workplace safety. Whether you need hazardous materials training, fall protection courses, confined space training in Vancouver, or Occupational First Aid Level 1, 2, and 3 courses, Metro Safety Training has the expertise and resources to meet your needs. Contact Metro Safety Training today to learn more about our comprehensive training programs and how we can help you create a safer workplace.