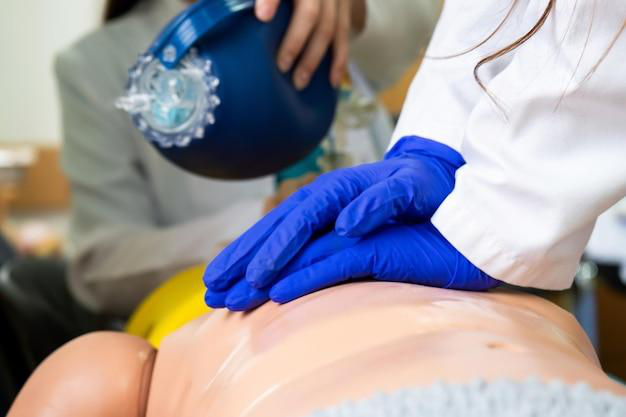
In Canada, workplace safety regulations require employers to provide adequate First Aid resources for their employees. These resources often include well-trained staff capable of responding to emergencies.
However, navigating the complex regulatory requirements for advanced First Aid can be challenging for organizations, especially for those operating in industries with heightened risks like construction, manufacturing, and forestry.
This blog will take an in-depth look at the intricate regulatory landscape for Occupational First Aid level 3 (Advanced First Aid),
The Importance of First Aid Compliance
First Aid Compliance refers to adherence to regulatory standards set by governing bodies that ensure workplaces are equipped with proper First Aid resources. In Canada, occupational health and safety (OHS) regulations are mandated at both the federal and provincial levels, each with its own set of requirements for First Aid training and certification. Employers must understand the legal frameworks that apply to their business to ensure full compliance.
Regulatory Bodies Governing First Aid Compliance in Canada
The regulations surrounding occupational advanced First Aid are governed by various bodies at the federal, provincial, and territorial levels. These regulatory bodies set the standards for First Aid training and equipment that must be available in workplaces based on the nature of the work and the number of employees.
WorkSafeBC
For businesses in British Columbia, WorkSafeBC plays a significant role in regulating First Aid training courses and equipment standards. The regulatory framework is detailed and mandates that specific workplaces, particularly those in high-risk industries, provide occupational advanced First Aid courses for select employees.
Provincial Guidelines
Other provinces, including Ontario, Alberta, and Manitoba, also have their First Aid compliance requirements, generally managed by bodies like the Ministry of Labour and respective Workers’ Compensation Boards (WCB). These regulations may vary slightly, particularly in the specific certification requirements and renewal timelines, but they all share a common goal: ensuring that workplaces have adequately trained First Aid personnel.
Federal OHS Regulations
At the federal level, the Canada Occupational Health and Safety Regulations (COHSR) also set out minimum standards for First Aid in federally regulated industries such as transportation, telecommunications, and banking. These regulations are overseen by Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) and ensure uniformity across various sectors.
Federal guidelines require that all employees in federally regulated industries have access to adequate First Aid resources, including First Aid training courses and certified First Aid attendants who can handle workplace injuries until professional medical help arrives.
Compliance Strategies for Employers
Navigating these complex regulations can be challenging, particularly for large organizations that operate in multiple provinces with varying regulations. However, there are several strategies that employers can adopt to ensure compliance:
1. Conducting a Risk Assessment
The first step toward ensuring compliance with First Aid regulations is conducting a comprehensive risk assessment of your workplace. A risk assessment will identify the potential hazards employees may face and determine the level of First Aid resources required.
High-risk environments, such as construction sites or factories, will require more advanced First Aid measures compared to office settings. These measures may include having multiple employees certified through occupational advanced First Aid courses and ensuring access to life-saving equipment like automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
2. Establishing a Fall Protection Safety Plan
One specific regulatory requirement for high-risk industries is the establishment of a fall protection safety plan. Falls are one of the most common causes of workplace injuries, and employers must ensure that they have adequate fall protection measures in place, including fall arrest systems and fall protection training for employees.
A fall protection safety plan outlines how employees are protected from fall hazards, what equipment is used, and the procedures to follow in case of an emergency. As part of this plan, employees must receive the appropriate level of First Aid training, including occupational advanced First Aid, to respond effectively to injuries resulting from falls.
3. Choosing the Right First Aid Training Provider
One of the most critical steps in ensuring compliance is selecting a reputable training provider for your First Aid courses. Not all training programs are created equal, and it’s important to choose a provider that meets the regulatory standards set by bodies like WorkSafeBC and other provincial authorities.
When choosing a training provider, make sure they offer a range of First Aid training courses that meet the specific needs of your workplace.

4. Keeping Certifications Up to Date
First Aid certifications are not permanent and require regular renewal. Most certification bodies, including WorkSafeBC, have guidelines on the renewal timelines for different levels of certification. For example, occupational advanced First Aid certificates typically need to be renewed every three years, while basic First Aid training may have a shorter renewal period.
Employers should keep a record of all First Aid certifications within their organization and establish a system to remind employees when their certifications are about to expire. Keeping certifications up to date ensures that your workplace remains compliant with provincial regulations and that your employees are always prepared to respond to emergencies.
Certification Requirements for Advanced First Aid
Understanding the certification requirements for advanced First Aid is essential for employers and employees alike. The certification process ensures that First Aid attendants are adequately trained to respond to emergencies in the workplace, particularly in high-risk environments.
Occupational First Aid Level 3 (Advanced First Aid)
This is the most advanced level of First Aid certification in British Columbia, designed for workplaces where employees may be exposed to significant risks of serious injuries. This course equips participants with the skills needed to respond to life-threatening injuries, including fractures, spinal injuries, and severe bleeding.

Participants must complete a comprehensive training program and pass both written and practical examinations to earn their certification. The training covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Emergency scene management
- Spinal and head injuries
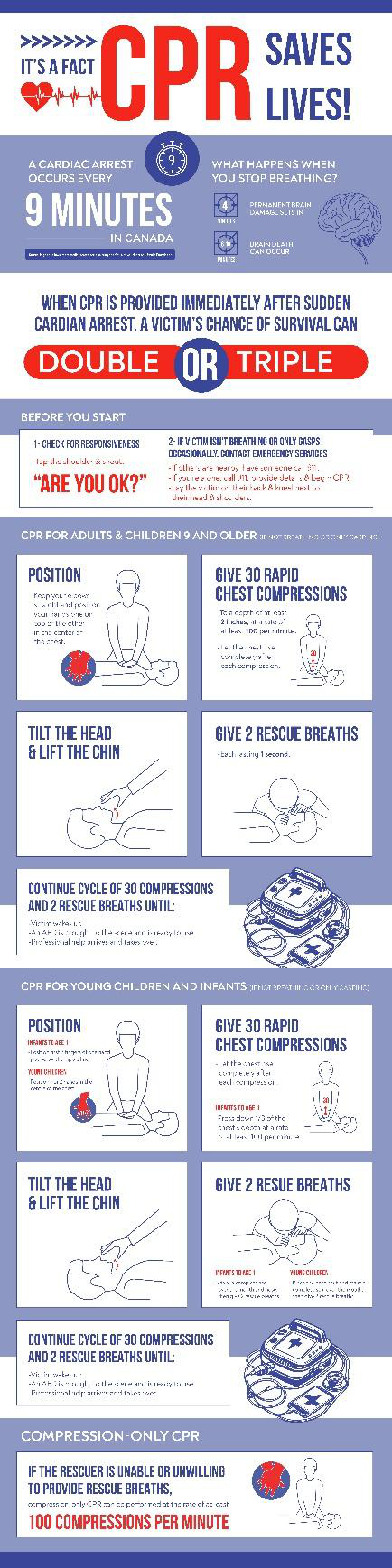
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and AED usage
- Treatment of fractures, dislocations, and sprains
- Control of severe bleeding
- Use of advanced First Aidequipment like oxygen tanks and suction units
To ensure compliance, employers must designate a certain number of employees to hold Occupational advanced First Aid certification, based on the size of the workforce and the nature of the work being performed.
Basic First Aid Training
For lower-risk workplaces, basic First Aid training is often sufficient to meet regulatory requirements. This level of certification covers the fundamental skills required to respond to common workplace injuries, such as minor cuts, burns, and choking. The course typically lasts one to two days and includes practical assessments to ensure that participants can apply their knowledge in real-life scenarios.
Emergency First Aid (EFA) Course
The Emergency First Aid (EFA) course is another essential training program that focuses on providing life-saving skills in emergencies. This course is often required for workplaces where employees may face immediate dangers but are not regularly exposed to high-risk activities.
The Emergency First Aid (EFA) course covers basic emergency response techniques, including CPR, bleeding control, and how to treat shock. For many organizations, this level of training meets the minimum regulatory requirements for First Aid compliance, particularly in office environments or retail settings.
Best Practices for Maintaining First Aid Compliance
Ensuring compliance with First Aid regulations is an ongoing process that requires employers to stay informed about changing regulations and best practices. Here are some key strategies for maintaining compliance:
1. Regular Training and Drills
First Aid training should not be a one-time event. Regular training sessions and emergency drills help employees retain their skills and remain prepared for real-life emergencies. Scheduling periodic refresher courses and drills can help maintain a high level of readiness in your workforce.

2. Keep First Aid Kits Well-Stocked
Having certified First Aid attendants is only one part of the compliance equation. Employers must also ensure that First Aid kits are well-stocked with all the necessary supplies. First Aid kits should be checked regularly, and any used or expired items should be promptly replaced.
3. Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes
First Aid regulations can change over time, and employers must stay updated on any changes that may affect their compliance. Regularly reviewing the guidelines set by provincial and federal regulatory bodies can help you stay ahead of potential compliance issues.
Ready to ensure that your workplace meets regulatory requirements for First Aid compliance? Contact Metro Safety Training today to learn more about our comprehensive First Aid training courses in Surrey and how we can help your team stay prepared for any emergency. Stay compliant, stay safe!